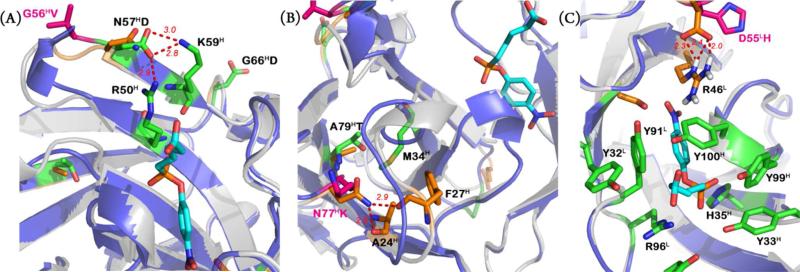
Figure 3.
Close-up views of key interactions: (A) The somatic mutation N57HD introduces hydrogen-bonding interactions with residues R50H and K59H. (B) The somatic mutation N77HK results in the loss of two hydrogen bonds with residues A24H and F27H in the germline structure. The somatic mutation A79HT enhances hydrophobic interactions with M34H. (C) The hydrophobic linker of JWJ1 is surrounded by four key tyrosine residues (Y32L, Y91L, Y99H, and Y100H). Within this hydrophobic pocket lie H35H and R96L, which form an oxyan ion hole in which binds the phosphonate group. Mutation D55LH removes hydrogen-bonding interactions with R46L.