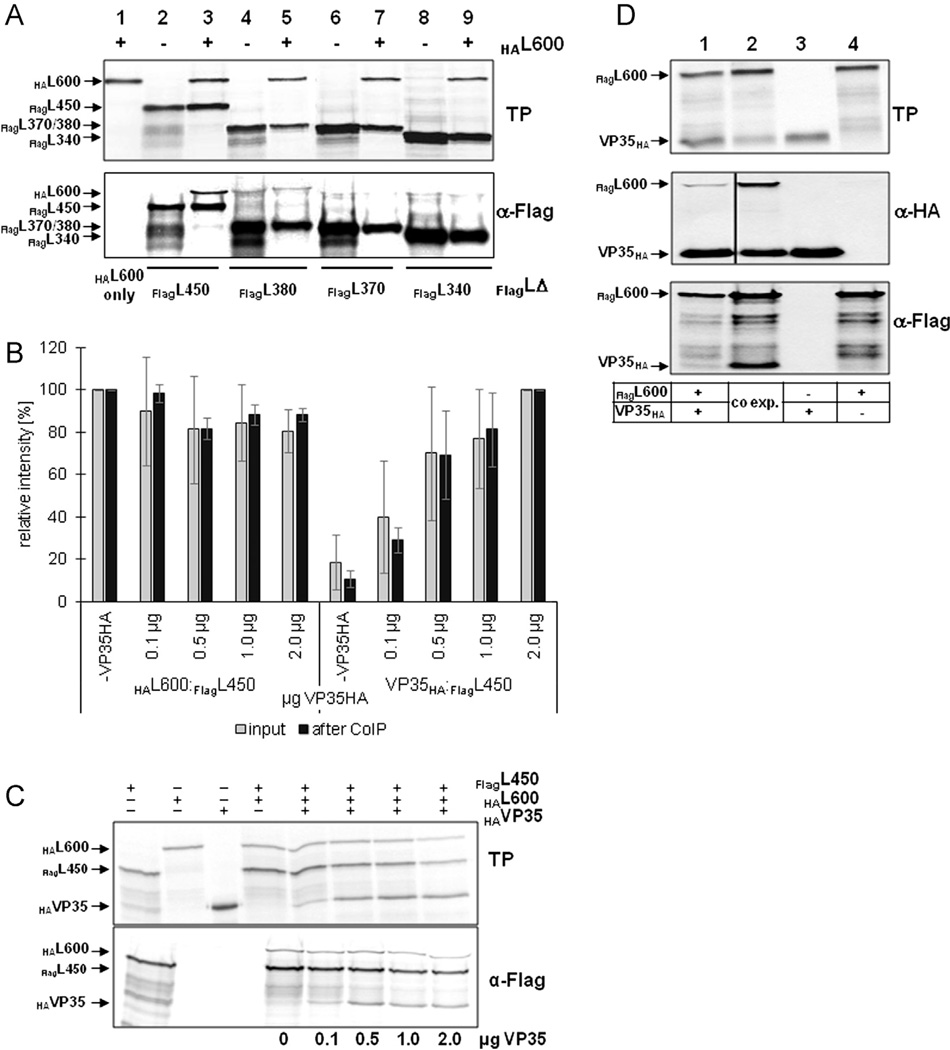
Fig. 5.
The homo-oligomerization domain in the N-terminus of EBOV L does not compete with VP35 binding. (A) In vitro translation products (TP) and CoIP analysis of HAL600 with various FLAG-tagged L fragments using an anti-FLAG antibody. (B) Impact of VP35HA on L homo-oligomerization. HAL600 and FlagL450 were in vitro translated in the presence of increasing amounts of VP35HA. The ratio of HAL600 and VP35HA relative to FlagL450 was determined before (gray bars) and after (black bars) CoIP with an anti-FLAG antibody. The average of three experiments is shown with standard deviations. (C) Representative gels used for the quantification shown in Fig. 5B. Upper panel, in vitro translation products (TP); bottom panel, CoIP using an anti-FLAG antibody. (D) Comparison of expression and coprecipitation levels of FlagL600 and VP35HA when expressed separately (lane 1) or concurrently (lane 2). Single expression is shown in lanes 3 and 4. The experiment was performed three times and a representative gel is shown.