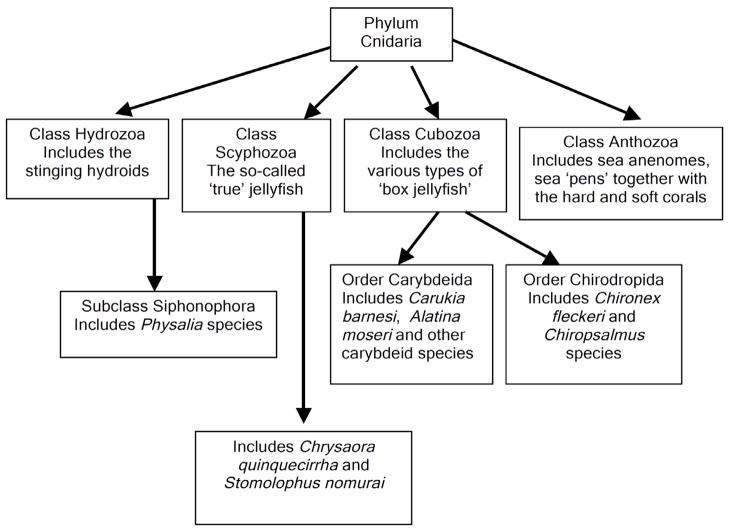
Fig. 1.
Taxonomic overview of medically and toxinologically significant jellyfish, placed in the context of the other major Cnidarian classes. This phylum is one of the oldest living animal groups with major classes extant in Precambrian times. Cnidarians are characterised by the presence of radial symmetry, two cell layers (ecto- and endoderm) with a single body cavity. They are primarily predatory organisms possessing cnidae, an intracellular capsule elaborated by the Golgi apparatus. Specialised cnidae (nematoblasts) elaborate a “stinging cell” (nematocyst) for the purposes of defence and capture of prey. It is these nematocysts that contain diverse and potent venoms.