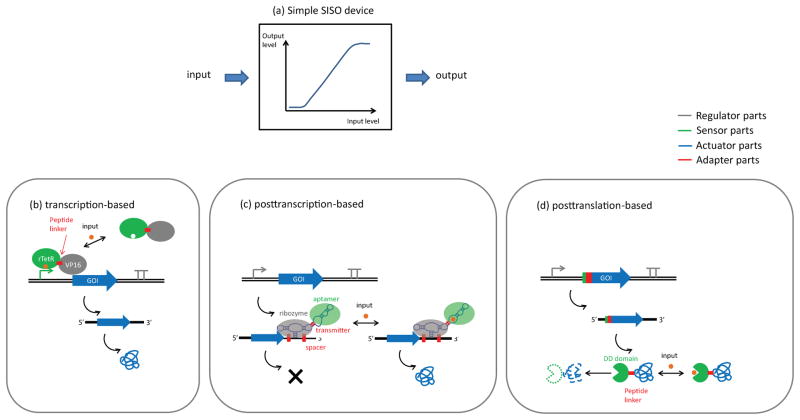
Figure 1.
A single-input, single output (SISO) device. (a) The input/output curve of the SISO device. (b) A transcription-based scheme for implementing SISO. An inducible transcriptional activator is composed of a ligand-binding protein (sensor) fused with an RNA polymerase recruiting domain (regulator). Binding of the input ligand enables the sensor binding to its corresponding promoter region, which turns on gene expression. (c) A posttranscription-based scheme for implementing SISO. An RNA aptamer (sensor) is coupled with a ribozyme (regulator) through an RNA transmitter sequence (adapter). This device is turned on in the presence of input molecule, which binds to the sensor and disrupts the self-cleaving confirmation of the regulator. (d) A posttranslation-based scheme for implementing SISO. A protein destabilizing domain (sensor) is fused directly to the gene-of-interest (actuator) with a peptide linker (adapter). The input ligand can bind to the destabilizing domain; thus prevents the protein from degradation.