Fig. 2.
Correlation of the ABCA4 transporter with lipofuscin bis-retinoid biosynthesis
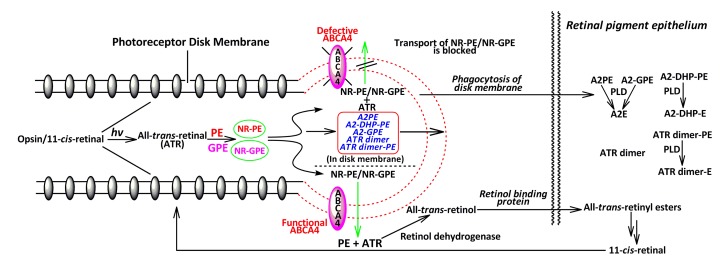
All-trans-retinal (ATR) comes from the isomerization of 11-cis-retinal that is released from light-activated rhodopsin in the retina. Incubation of ATR with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)/glycerophosphoethanolamine (GPE) would give rise to N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (NR-PE)/N-retinylidene-glycerophosphoethanolamine (NR-GPE) that can be delivered to the cytoplasmic side of disk membranes by ABCA4. When the activity of this transporter attenuates or becomes extinct, NR-PE and NR-GPE have no choice but to reside in the rod outer segments, and react with a second molecule of ATR to form various bis-retinoids including N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-phosphatidylethanolamine (A2PE), N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-dihydropyridine-phosphatidylethanolamine (A2-DHP-PE), N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-glycerophosphoethanolamine (A2-GPE), ATR dimer, and ATR dimer-PE via a multi-step cascade. Rod outer segments are routinely discarded on a daily basis, and subsequently are phagocytosed by RPE cells, resulting in the transfer of these di-retinal pigments to RPE where PLD, a lysosomal acid enzyme, can cleave A2PE, A2-GPE, A2-DHP-PE, and ATR dimer-PE to produce N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-ethanolamine (A2E), N-retinylidene-N-retinyl-dihydropyridine-ethanolamine (A2-DHP-E), and ATR dimer-E, respectively. However, ATR dimer remains intact due to the inability to be further digested by the lysosomal enzymes