Figure 5.
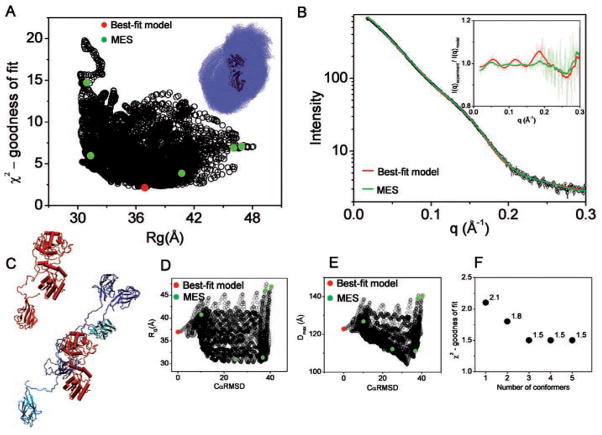
BILBOMD analysis of mammalian polynucleotide kinase (mPNK). A. Graph represents the comparison of discrepancy (χ2) values for 6000 mPNK models with their RG values. The value for best-fit model is indicated by red dot. The green dots indicate the five MES conformers. Inset – the superimposition of all 6000 nPNK modeled comnformers. FHA domains are shown in blue dot representation. PK is shown in carton colored (red). B. Experimental SAXS curve (black). Red and green lines represent theoretical scattering for the best-fit and MES ensemble, respectively. Inset – calculated residuals (I(q)experiment/I(q)model) for MES ensemble with 5 conformers and single best-fit model. For better visualization the residuals have been smoothed. C. The best-fit model for mPNK (left panel). The five MES-selected models, representing conformational space of the FHA domain (colored blue). The models are superimposed on the PK structure colored red (right panel). D., E. Graph represents the comparison of RG and Dmax values for all 6000 models with their CαRMSD values referenced to the best-fit model. The values for the best-fit model and MES-selected models are indicated by red and green dots, respectively. F. χ2 values for MES fit in dependence to the number of selected conformers.