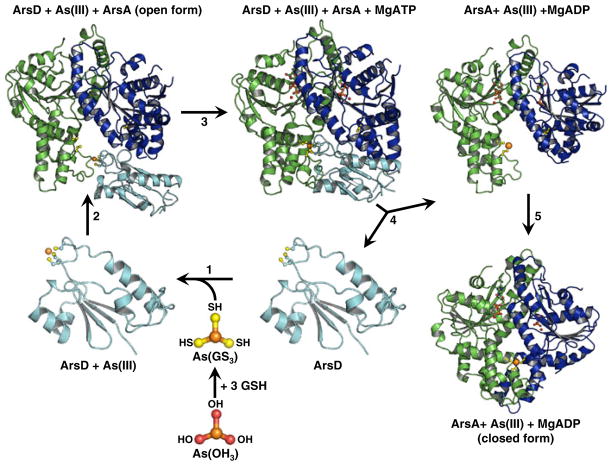
Fig. 1.
Proposed reaction scheme for transfer of As(III) from ArsD to ArsA. In the cytosol As(OH)3, the solution form or arsenite, reacts with 3 GSH to form As(GS)3, the arsenic donor to ArsD (Yang et al. 2010). Step 1 ArsD binds As(III) by exchange of the three thiols of As(GS)3 for the thiols of cysteines residues Cys12, Cys13 and Cys18. Although ArsD is a dimer, the structure of the monomer of apoArsD is shown (Ye et al. 2010). Step 2 As(III)-bound ArsD binds to the open form of ArsA. Step 3 As(III) is transferred in a step-wise exchange from the three thiols of ArsD to the thiols of Cys113, Cys172 and Cys422 of ArsA. Step 4 Transfer of As(III) results in dissociation of the ArsD-ArsA complex. Step 5 As(III)-bound ArsA undergoes a conformational change in ArsA to the closed form concomitant with activation of ATP hydrolysis