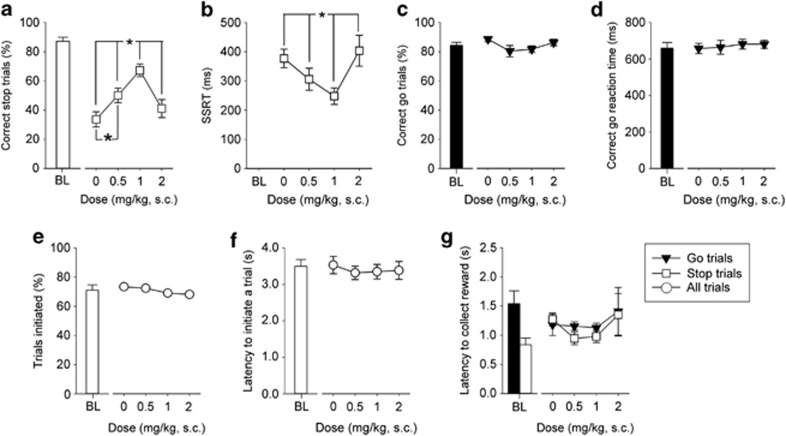
Figure 5.
Effects of SB242084 on SSRTT performance. SB242084 (6-chloro-5-methyl-1-[2-(2-methylpyridyl-3-oxy)-pyrid-5-yl carbomyl] indoline, Sigma, UK) was administered (s.c.) immediately prior to testing in sessions where the stop-signal position was at 50% of the go response. Animals were given a single session with each dose of drug, based on a Latin square design, with at least 4 days of stable performance and baseline criteria between each treatment. All concentrations were calculated as free base and made up in physiological saline fresh on the day of use. Increasing doses of SB242084 up to 1 mg/kg improved stopping behavior (a) and decreased SSRT (b), whereas the highest 2 mg/kg dose was ineffective. There was no effect of SB242084 on correct go trials (c), correct go reaction time (d), the number of trials initiated (e), the latency to initiate a trial (f) or reward collection latencies (g). Baseline data (BL—mean of the five sessions immediately preceding each drug treatment session) when the stop-signal presentation was concurrent with the start of the go response (ie, at 0%) are shown for illustrative purposes and were not included in the statistical analysis. Data are mean±SEM, n=13. *p<0.05 for pairwise differences related to dose of drug.