Fig. 1.
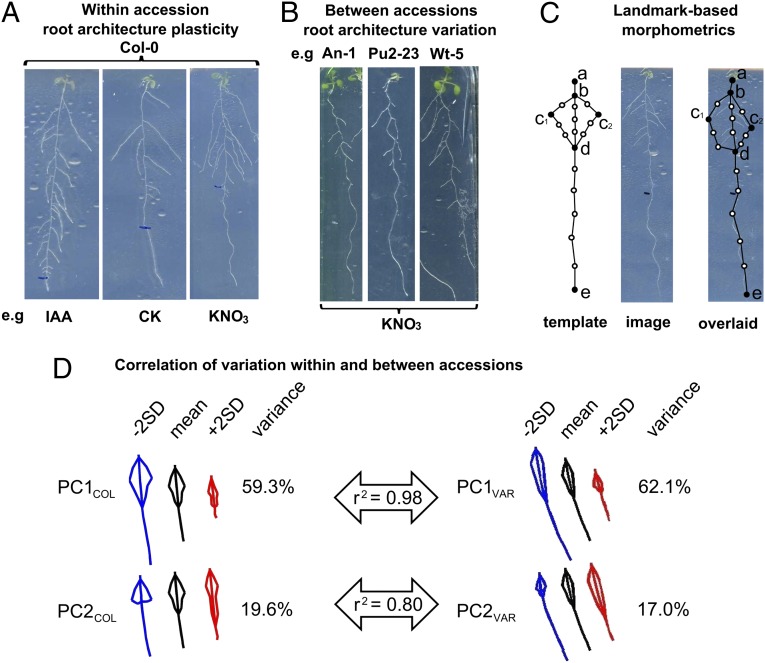
Root architecture plasticity within an accession (Col-0) broadly recapitulates natural variation quantified across 69 accessions. (A) Root phenotypes of Col-0 plants were grown under five conditions: IAA, CK, ABA, KNO3, and NH4Cl plus a control (KCl); roots of three treatment conditions are shown. (B) Root variation between 69 accessions grown under one condition (KNO3). (C) Landmark template to capture the root system architecture (11). Primary landmarks (black circles) are defined according to corresponding features in all roots; secondary landmarks (white circles) are evenly spaced between primary landmarks (11). (D) Two PCs capture more than 75% of the variation both within Col-0 (PCCOL) and between accessions (PCVAR). PC1COL and PC2COL have high correlation to PC1VAR and PC2VAR, respectively. PC1COL is mainly a size effect, whereas PC2COL captures mainly root allometry, the length and distribution of lateral roots long the primary root. SD, standard deviation.