Table 1.
Effects of experimental JA spray in this study, and natural defoliation in a previous study (17), on percent hydrolyzable tannin concentration in red oak foliage
| Induction method | Treatment | Pretreatment concentration, % | Posttreatment concentration, % |
| JA spray | JA | 19.7 ± 0.82 | 27.8 ± 0.82 |
| Control | 19.5 ± 0.74 | 15.9 ± 0.84 | |
| Natural defoliation | Defoliated | 23.30 ± 1.0 | 27.05 ± 1.4 |
| Ref. 17 | Control | 23.36 ± 0.9 | 19.54 ± 0.9 |
Pretreatment concentrations were significantly different between studies (treatments, 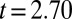 ,
, 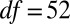 ,
, 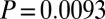 ; controls,
; controls, 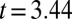 ,
, 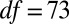 ,
, 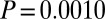 ), as were posttreatment control concentrations (
), as were posttreatment control concentrations (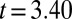 ,
, 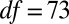 ,
, 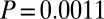 ), reflecting natural background variability in hydrolyzable tannins. Posttreatment concentrations were nevertheless effectively identical in JA-sprayed and naturally defoliated branches (
), reflecting natural background variability in hydrolyzable tannins. Posttreatment concentrations were nevertheless effectively identical in JA-sprayed and naturally defoliated branches (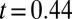 ,
,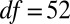 ,
, 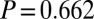 ), and controls in the two studies declined by similar magnitudes.
), and controls in the two studies declined by similar magnitudes.
