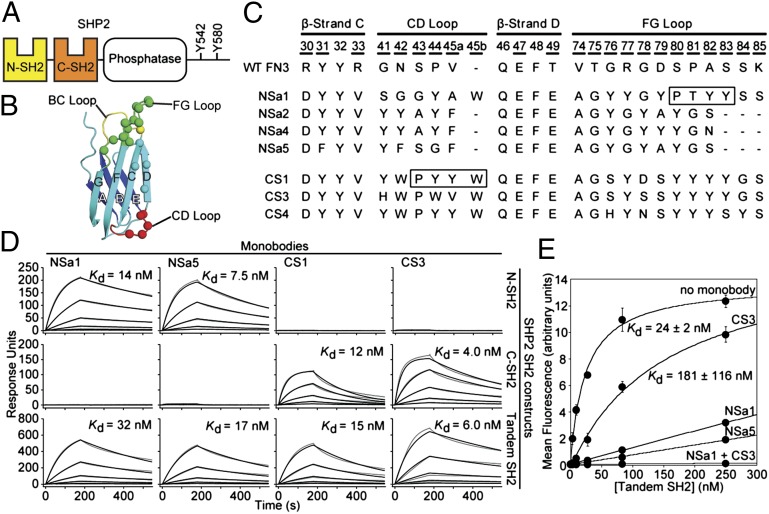
Fig. 1.
Generation of SHP2 SH2-binding monobodies. (A) Domain organization of SHP2. (B) Schematic of the FN3 scaffold. The β-strands are labeled A–G, and diversified residues are shown as colored spheres. (C) Amino acid sequences of selected monobody clones and WT FN3. Residue numbers for diversified positions are underscored. The N series and C series monobodies are directed to the N-SH2 and C-SH2 domains, respectively. The boxes denote segments that bind to the peptide-binding site of the SH2 domains in the crystal structures. (D) SPR sensorgrams and dissociation constants for monobody binding to SHP2 SH2s. Parameters from the best fit of a 1:1 binding model (black traces) to the raw data (gray traces) are given in SI Appendix, Table S1. (E) Binding of the tandem SHP2 SH2 domains to a GAB2 fragment containing tandem pY sites (residues Y614 and Y643) in the absence and presence of saturating concentrations of the indicated monobodies.