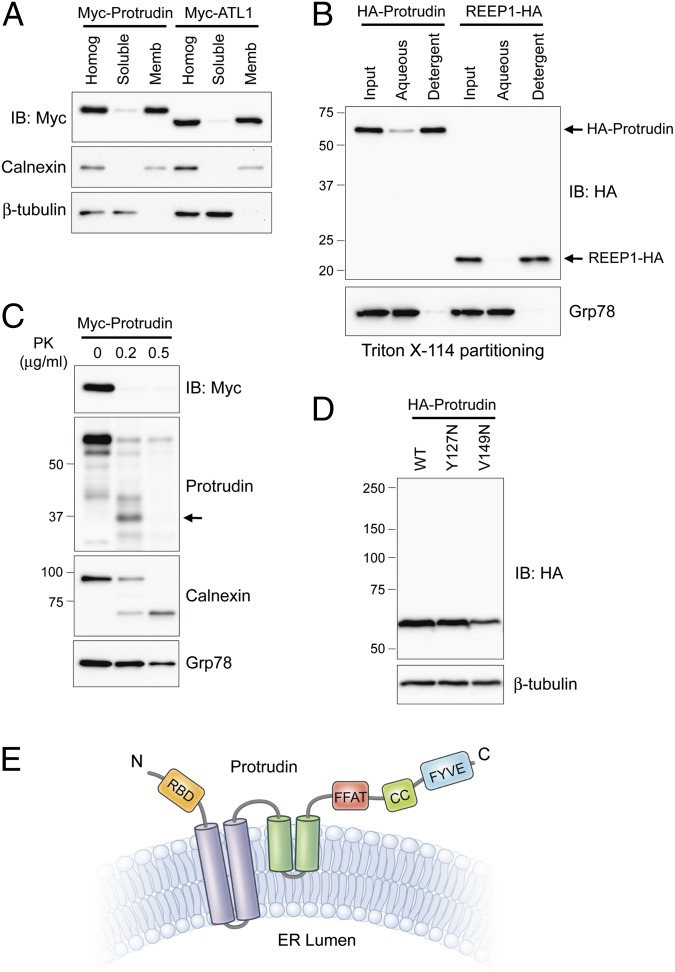
Fig. 1.
Membrane topology of protrudin. (A) Myc-tagged protrudin or atlastin-1 were transfected into HEK293T cells as indicated. Homogenates (Homog) were resolved into soluble and membrane (Memb) fractions, and aliquots were immunoblotted (IB). Calnexin and β-tubulin are markers for membrane and cytosolic fractions, respectively. (B) Membrane fractions from cells expressing HA-protrudin or REEP1-HA were phase partitioned with Triton X-114 and then immunoblotted for HA-epitope or Grp78. (C) Protease protection assays. Microsomes from Myc-protrudin–expressing cells were treated with PK. Aliquots were immunoblotted with Myc-epitope (N terminus of protrudin) or anti-protrudin (C-terminal region of protrudin) antibodies. Calnexin (partly luminal) and Grp78 (completely luminal) were used to monitor proteolysis. A major proteolytic fragment of protrudin is denoted with an arrow. (D) Cells were transfected with wild-type (WT) Myc-protrudin or else Y127N and V149N mutants, and lysates were immunoblotted as shown. (E) Membrane topology model for protrudin. CC, coiled-coil; RBD, Rab-binding domain. Migrations of molecular-mass standards (in kilodaltons) are to the left in B–D.