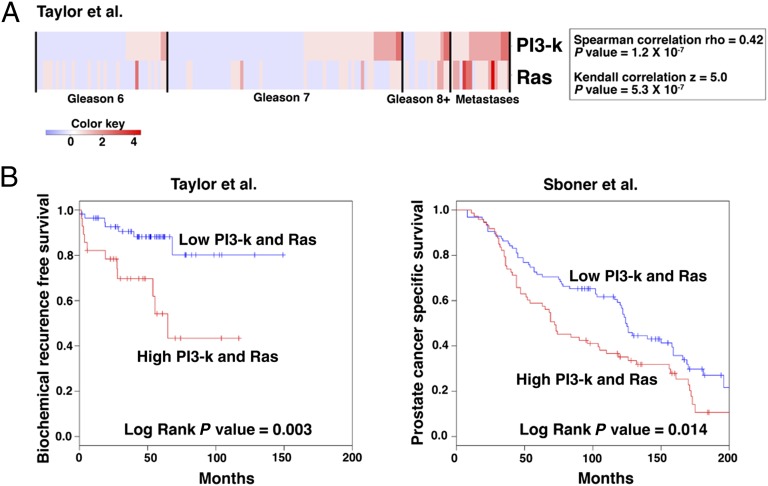
Fig. 1.
Coactivation of PI3-kinase and Ras signaling pathways is associated with adverse patient outcome. (A) Correlation of PI3-kinase and Ras signaling in human prostate cancer from the Taylor et al. (6) dataset. Shown is a heat map in which each clinical sample (i.e., primary tumors of the indicated Gleason scores and metastases) was evaluated to determine status for PI3-kinase and Ras signaling (Materials and Methods). Correlation coefficients and P values of the correlations are shown for both Spearman rho and Kendall z calculations. The color key indicates relative expression levels of the pathway. (B) Kaplan–Meier analyses showing the association of activation of both PI3-kinase and Ras signaling with adverse patient outcome in two independent cohorts using biochemical recurrence-free (BCR-free; Left) and prostate cancer-specific survival (Right) as clinical endpoints.