Fig. 7.
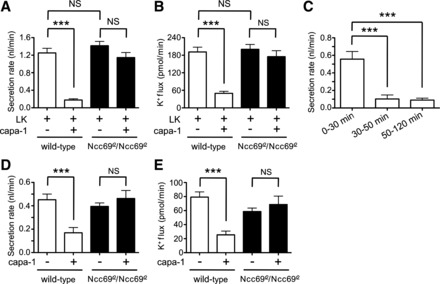
The antidiuretic and antikaliuretic effects of capability-1 (capa-1) are Ncc69 dependent. A: secretion rates (nl/min per tubule) were measured in tubules from wild-type and Ncc69r2 homozygous mutants in the presence of 10−7 M leucokinin (LK), in the absence (n = 15–17) or presence (n = 30–32) of 10−7 M capa-1. There is no difference in leucokinin-stimulated secretion between wild-type and Ncc69 mutant tubules, but the antidiuretic effects of capa-1 are abolished in Ncc69 mutant tubules. ***P < 0.001. For the difference between leucokinin- and capa-1-treated wild-type and Ncc69r2/Ncc69r2, P < 0.001. B: K+ flux (pmol/min per tubule) was measured in tubules from wild-type and Ncc69r2 homozygous mutants in the presence of 10−7 M leucokinin, in the absence (n = 15–17) or presence (n = 30–32) of 10−7 M capa-1. There is no difference in leucokinin-stimulated K+ flux between wild-type and Ncc69 mutant tubules, but the antikaliuretic effects of capa-1 are abolished in Ncc69 mutant tubules. ***P < 0.001. For the difference between leucokinin- and capa-1-treated wild-type and Ncc69r2/Ncc69r2 tubules, P < 0.001. C: secretion rate (nl/min per tubule) was serially measured in wild-type tubules (n = 22) treated with 10−7 M leucokinin and 10−7 M capa-1 over 0–30 min, 30–50 min, and 50–120 min. The antidiuretic effect is apparent after 30 min. ***P < 0.001. The difference between 30–50 min and 50–120 min was NS. D: secretion rates (nl/min per tubule) were measured in wild-type and Ncc69r2 homozygous mutants in the absence or presence of 10−7 M capa-1 (n = 10–11 tubules per genotype/condition). Capa-1 inhibited secretion in wild-type, but not Ncc69 mutant tubules. ***P < 0.001. E: K+ flux (pmol/min per tubule) was measured in wild-type and Ncc69r2 homozygous mutants in the absence or presence of 10−7 M capa-1 (n = 10–11 tubules per genotype/condition). Capa-1 inhibited K+ flux in wild-type, but not Ncc69 mutant tubules. ***P < 0.001.
