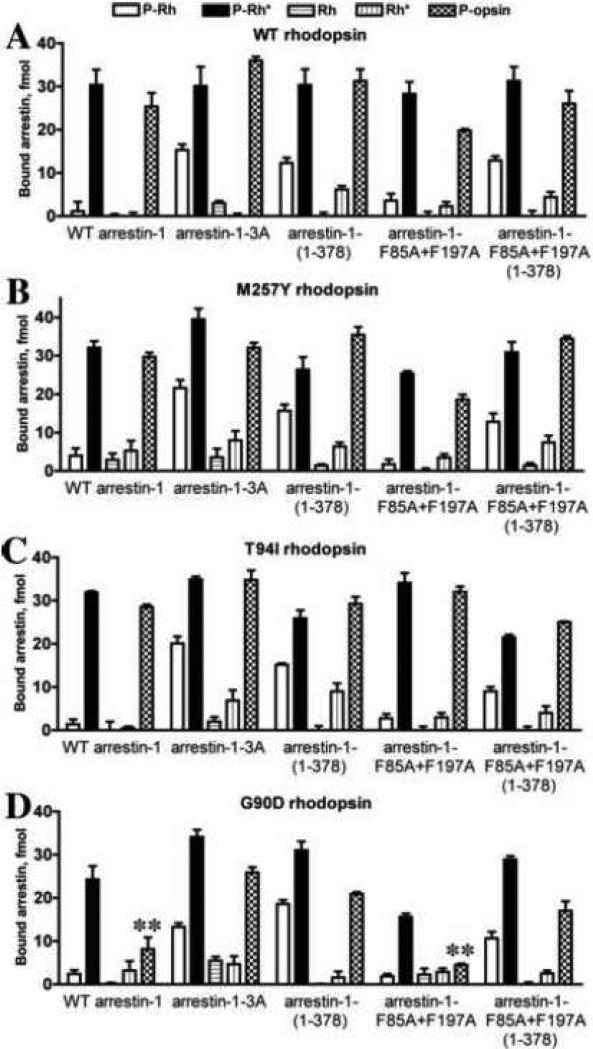
Fig. 3. The binding of arrestin-1 mutants to five functional forms of WT rhodopsin and three constitutively active variants.
A. Translated radiolabeled WT arrestin-1 (WT) and indicated mutants (100 fmol) were incubated with 0.3 μg of WT rhodopsin (unphosphorylated, Rh and Rh*) or phosphorylated by GRK1 (P-Rh, P-Rh*, and P-opsin) in the dark (Rh and P-Rh) or room light (Rh*, P-Rh*, and phospho-opsin) in 50 μl at 37°C for 5 min. The samples were cooled on ice, and bound arrestins were separated from free by gel-filtration on 2-ml Sephadex G-100 columns, as described in methods. Bound arrestins eluted with rhodopsin-containing HDL particles were quantified by scintillation counting. B, C, D. The same experiment described in A was performed with M257Y, T94I, or G90D rhodopsin mutants, respectively. Means ± SD of two independent experiments performed in duplicate are shown in all panels. **, p<0.01, as compared to the binding of the same arrestin-1 (WT or F85A+F197A constitutively monomeric mutant) to p-Ops form of WT rhodopsin.