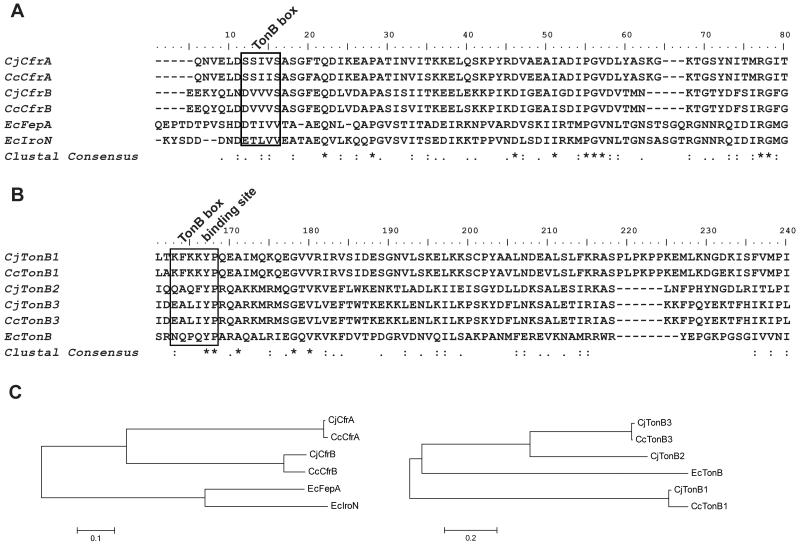
Figure 2.
Comparative analyses of FeEnt receptors and TonB components in Campylobacter and E. coli. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of FeEnt receptors from Campylobacter and E. coli. The sequences were aligned with Clustal W2. The region of aa 1-80 was displayed. Putative TonB box region was highlighted in the rectangle boxes. Identical amino acids are marked by an asterisk (*), and conserved and semi-conserved substitutions, substitutions are marked by colon (:) and a single dot (•), respectively. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of identified TonB components in Campylobacter and E. coli. The region of aa 161-240 was displayed. One putative TonB box binding site was highlighted in the rectangle box. (C) Phylogenetic analyses of FeEnt receptors and TonB components from Campylobacter and E. coli. Left panel, phylogenetic analysis of C. jejuni FeEnt receptors (CjCfrA and CjCfrB), C. coli FeEnt receptors (CcCfrA and CcCfrB), and E. coli FepA and IroN. Right panel, phylogenetic analysis of C. jejuni TonB (CjTonB1, CjTonB2, and CjTonB3), C. coli TonB (CcTonB1 and CcTonB3), and E. coli TonB (EcTonB).