Abstract
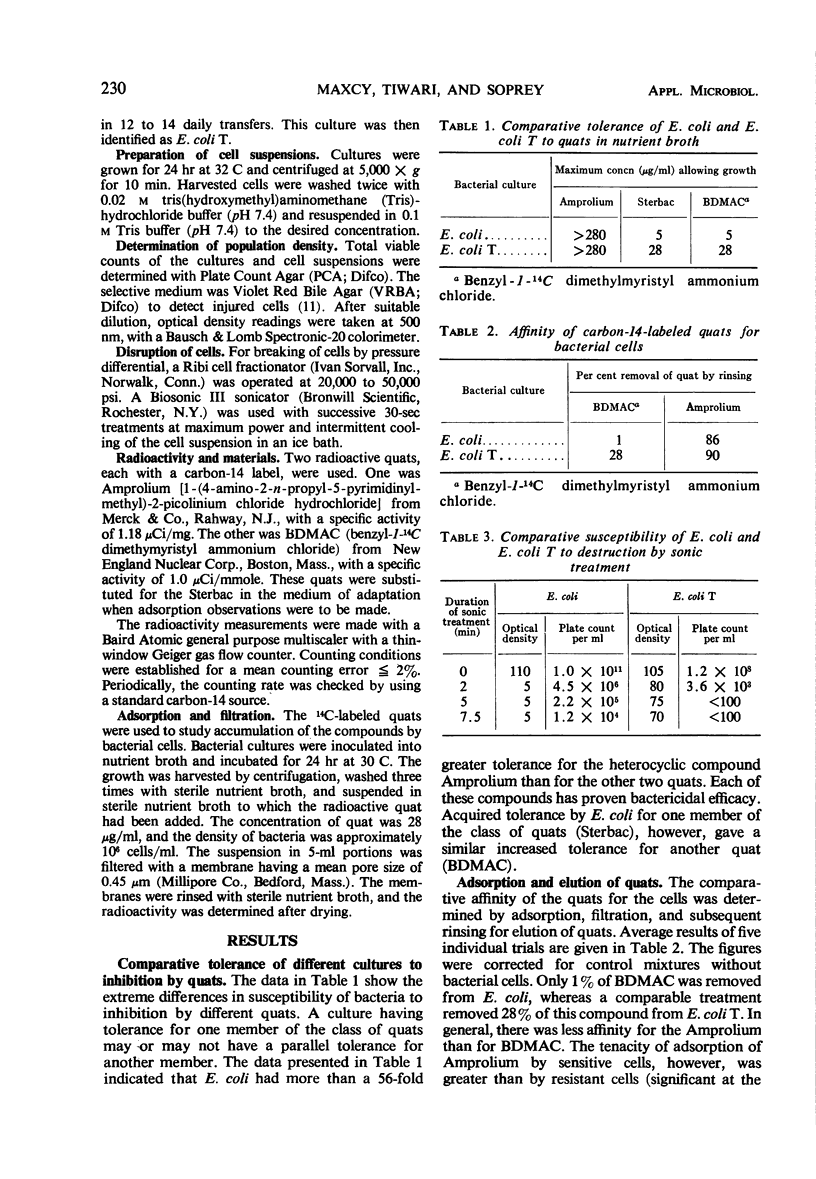
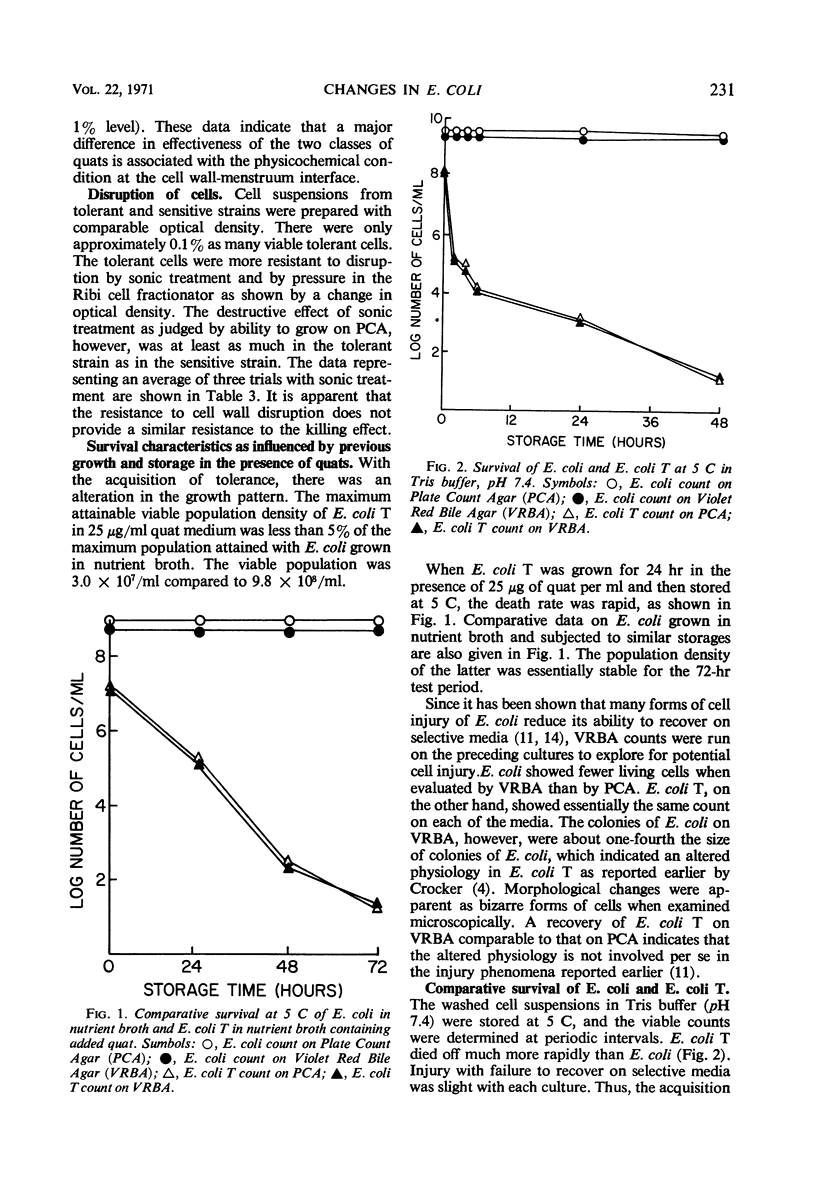
Acquired tolerance for a quaternary ammonium compound produced a tolerance for a similar compound. Tolerance was associated with the structure and the extent of adsorption of the compound. Morphological changes and resistance to disruption by pressure and by sonic treatment accompanied the development of tolerance. An otherwise weakened culture evolved with the acquisition of tolerance. The maximum obtainable viable population density of tolerant cells in growth medium was approximately 5% of that obtained in the parent culture. Tolerant cultures died off more rapidly in the original growth medium as well as when washed cell suspensions were stored at 5 C. Since acquired tolerance was associated with an otherwise weakened culture, the occurrence of the tolerant cells to limit the efficacy of quaternary ammonium compounds in sanitation operations is highly unlikely.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CEGLOWSKI W. S., LEAR S. A. Effects of a quaternary ammonium on Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1962 Sep;10:458–462. doi: 10.1128/am.10.5.458-462.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPLIN C. E. Bacterial resistance to quaternary ammonium disinfectants. J Bacteriol. 1952 Apr;63(4):453–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.4.453-458.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox W. A. Site of action of certain antibacterial heterocyclic quaternary ammonium compounds. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Nov;13(6):956–966. doi: 10.1128/am.13.6.956-966.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILBY A. R., FEW A. V. Lysis of protoplasts of Micrococcus lysodeikticus by ionic detergents. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:19–26. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J. Action of bile salts on bacterial cell walls. Nature. 1967 Jun 10;214(5093):1152–1154. doi: 10.1038/2141152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACGREGOR D. R., ELLIKER P. R. A comparison of some properties of strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sensitive and resistant to quaternary ammonium compounds. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Oct;4(5):499–503. doi: 10.1139/m58-054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxcy R. B., Dill C. W. Adsorption of free fatty acids on cells of certain microorganisms. J Dairy Sci. 1967 Apr;50(4):472–476. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(67)87449-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. J. The adsorption of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide by bacteria, its action in releasing cellular constituents and its bactericidal effects. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 May;5(2):391–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheusner D. L., Busta F. F., Speck M. L. Inhibition of injured Escherichia coli by several selective agents. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.46-49.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheusner D. L., Busta F. F., Speck M. L. Injury of bacteria by sanitizers. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):41–45. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.41-45.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


