Fig. 4.
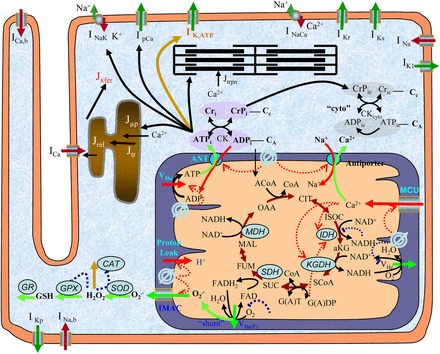
General scheme of the excitation-contraction coupling, mitochondrial energetics, and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced ROS release (ECME-RIRR) model. The electrophysiological module describes the major ion channels underlying the action potential (e.g., ATP-sensitive potassium channel) and the processes involved in Ca2+ handling (e.g., transport of Ca2+ across the sarcolemma, SR), and the inner mitochondrial membrane channels (e.g., Ca2+ uniport). The mitochondrial module accounts for the major components of mitochondrial energetics such as the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The RIRR module describes ROS production (from the electron transport chain), transport (through IMAC), and scavenging (e.g., by the superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase enzymes). The mitochondrial energetics and ROS are linked to cellular electrical activity through the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (KATP) current, which is activated when the ADP/ATP increases. Figure and legend are from Zhou et al. (255), used with permission. See Zhou et al. (255) for definitions of all abbreviations appearing in figure.
