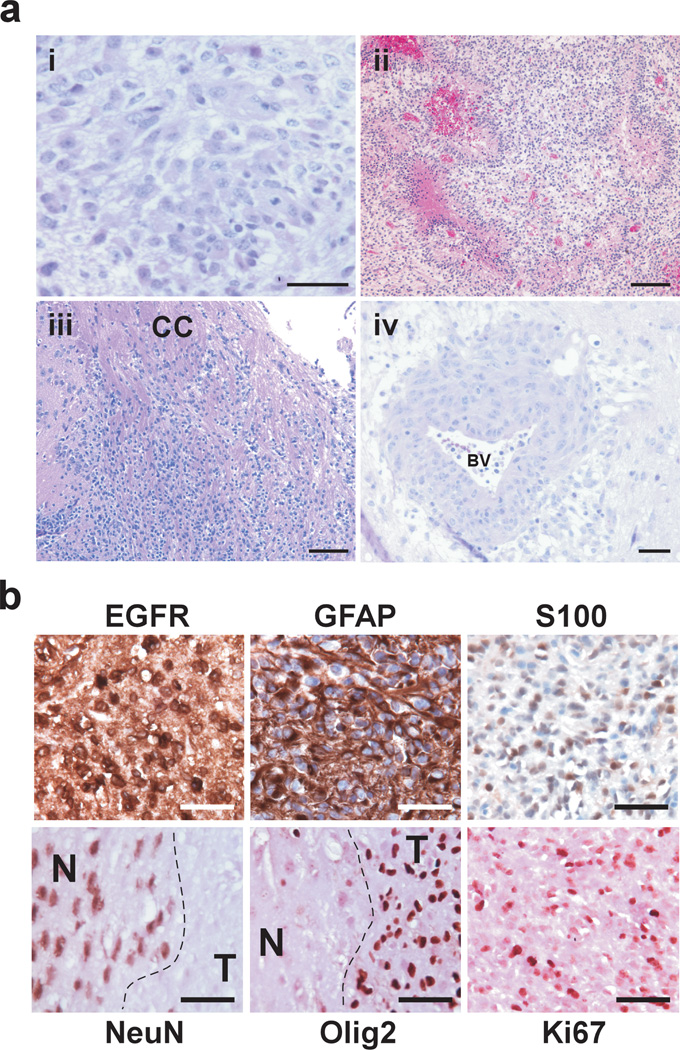
Figure 2.
Representative photomicrographs of H&E-stained histological sections of TGFα-EGFRWT tumors. (a) (i) Tumor cells are set on a fibrillary background and contain densely packed cells featuring pleomorphic nuclei with prominent nucleoli. (ii) Tumors exhibit marked pseudo pallisading necrosis. (iii-iv) The highly infiltrative nature of TGFα-EGFRWT tumor cells is depicted. (iii) Tumor cells migrate and infiltrate parenchyma along white matter tracks (corpus callosum CC) and (iv) migrate along blood vessels (BV) and invade the perivascular space. Scale bars; 50 µm (i,iv), 125 µm (ii, iii). (b) TGFα-EGFRWT tumors express markers of astrocytic differentiation. Representative photomicrographs of TGFα-EGFRWT tumors stained for the indicated cell lineage markers using immunohistochemistry. Tumors stain positive for the astrocytic lineage markers glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and S100 and negative for the neuronal lineage marker NeuN. Tumors also stain positive for human EGFR, the proliferation marker Ki67 and for Olig2. EGFR, GFAP and S100 sections were counterstained with hematoxylin and sections for the nuclear NeuN, Olig2 and Ki67 markers were counterstained with eosin. N, normal brain; T, tumor. Scale bars 50 µm.