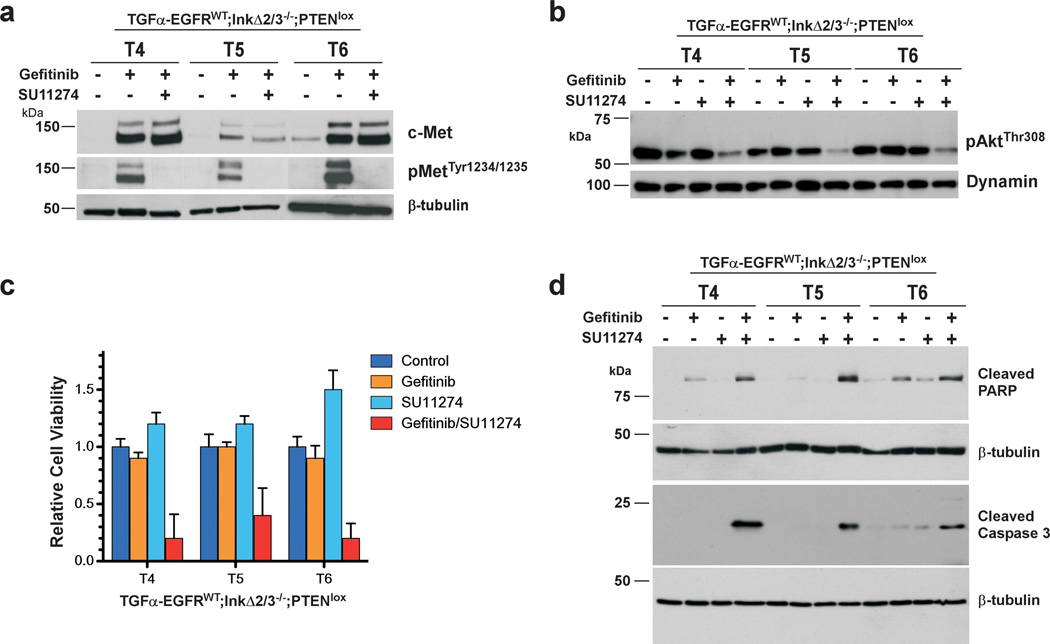
Figure 7.
Inhibition of c-MET sensitizes PTEN deficient tumor cells to EGFR TKI-induced apoptosis. PTEN deficient TGFα-EGFRWT;InkΔ2/3−/−;PTENlox GBM tumor cells were treated with gefitinib (10 µM) and/or the c-MET kinase inhibitor SU11274 (10 µM). (a) Immunoblot analysis of total cell lysates from TGFα-EGFRWT;InkΔ2/3−/−;PTENlox GBM tumor cells treated with the indicated inhibitors using c-MET and c-MET phosphotyrosine 1234,1235 antibodies. Anti β-tubulin probing is used as an internal loading control. (b) Activation of Akt is attenuated by inhibition of c-MET. Immunoblot analysis of total cell lysates against phospho Akt (Thr308) in TGFα-EGFRWT;InkΔ2/3−/−;PTENlox GBM tumor cells. Anti dynamin probing is used as an internal loading control. (c,d) Inhibition of c-MET induces apoptosis. Co-treatment of TGFα-EGFRWT;InkΔ2/3−/−;PTENlox GBM tumor cells with gefitinib and SU11274 causes a marked reduction in the relative viability of these cells (c). This reduced viability corresponds to an increase in the rate of drug-induced apoptosis (d) as demonstrated by immunoblot analysis of cleaved caspase 3 and cleaved PARP.