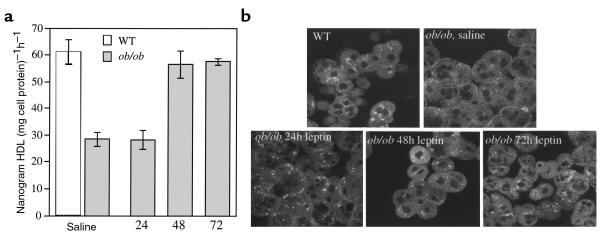
Figure 7.
Leptin restores the defect in HDL uptake by ob/ob primary hepatocytes and the altered localization pattern of HDL apoproteins in primary ob/ob hepatocytes. (a) ob/ob mice were injected twice daily with 1 μg/g body weight leptin for the times indicated. Control ob/ob mice (0 hour time point) were injected twice daily with saline and pair-fed to the leptin-treated mice. After treatments, hepatocytes were isolated and incubated with either apoE-free human 125I-HDL or Alexa-HDL (see Figure 6) at 37°C for 1 hour. Cells were then washed, and total cell radioactivity was counted. All experiments used 5 μg of HDL and were performed a total of 2–3 times in triplicate with similar results. Results were reported as mean nanogram of HDL per milligram of cell protein per hour ± SD, after subtraction of background counts measured in the presence of 100-fold excess unlabeled HDL (*0 and 24 hours versus 48 and 72 hours; P < 0.005). (b) Primary hepatocytes from a were incubated with Alexa-HDL at 37°C for 1 hour. Cells were then washed, fixed, and examined using confocal microscopy. Apoproteins in hepatocytes from leptin-treated ob/ob mice were localized in a similar pattern as seen in wild-type mice, i.e., juxtanuclear location. All experiments used 5 μg of HDL and were performed a total of 3 times with similar results.