Fig. 1.
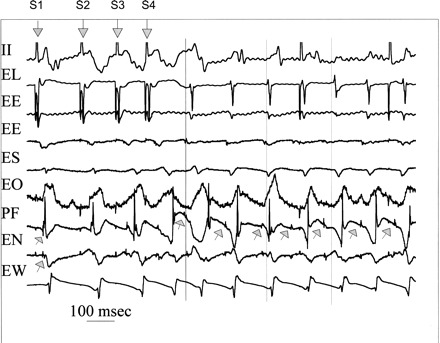
Induction of focal Purkinje ventricular tachycardia (VT) during angiotensin II (AGII) administration. Shown is the last pacing complex of the drive train and three extrastimuli (downward arrows labeled S1 through S4), and seven complexes of the induced VT. Recordings are surface ECG lead II and bipolar endocardial (E) electrograms from the lateral (L) site of pacing in the normal zone and ischemic zone recording sites east (E), south (S), overlying (O), north (N), and west (W) immediately surrounding (within 10 mm) the Purkinje (P) focus (F) of origin of VT. During the stimulated complexes, the upward arrows indicate Purkinje spikes (upward arrows), which are progressively delayed, along with the local muscle potentials. Site PF is the site of origin for the first and all subsequent VT complexes preceding the adjacent muscle activity. The vertical lines indicate surface QRS onsets for first, third, and fifth VT complexes to assist the reader. All activity surrounding PF occurs afterward and suggests focal activation with no very late activation that would be expected with reentrant excitation. See text for details.
