Fig. 1.
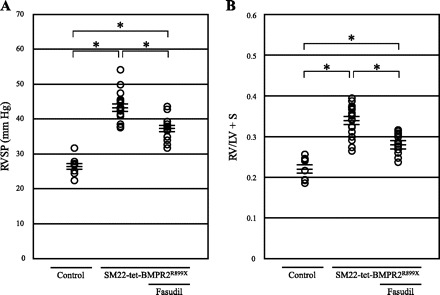
Treatment with fasudil alleviates pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy in transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor gene (with an arginine to termination mutation at amino acid 899) in smooth muscle by a tetracycline-gene switch system (SM22-tet-BMPR2R899X). A: right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) in SM22-tet-BMPR2R899X mice was elevated significantly (43.3 ± 1.0 mmHg, n = 20) compared with that in the controls (26.5 ± 0.8 mmHg, n = 10). Fasudil decreased RVSP in SM22-tet-BMPR2R899X mice (37.3 ± 0.9 mmHg, n = 14). B: the ratio of RV and left ventricle + ventricular septum (RV/LV + S) in SM22-tet-BMPR2R899X mice was elevated significantly (0.34 ± 0.01) compared with that in the controls (0.22 ± 0.01). Fasudil decreased RV/LV + S in SM22-tet-BMPR2R899X mice (0.28 ± 0.01). *P < 0.01.
