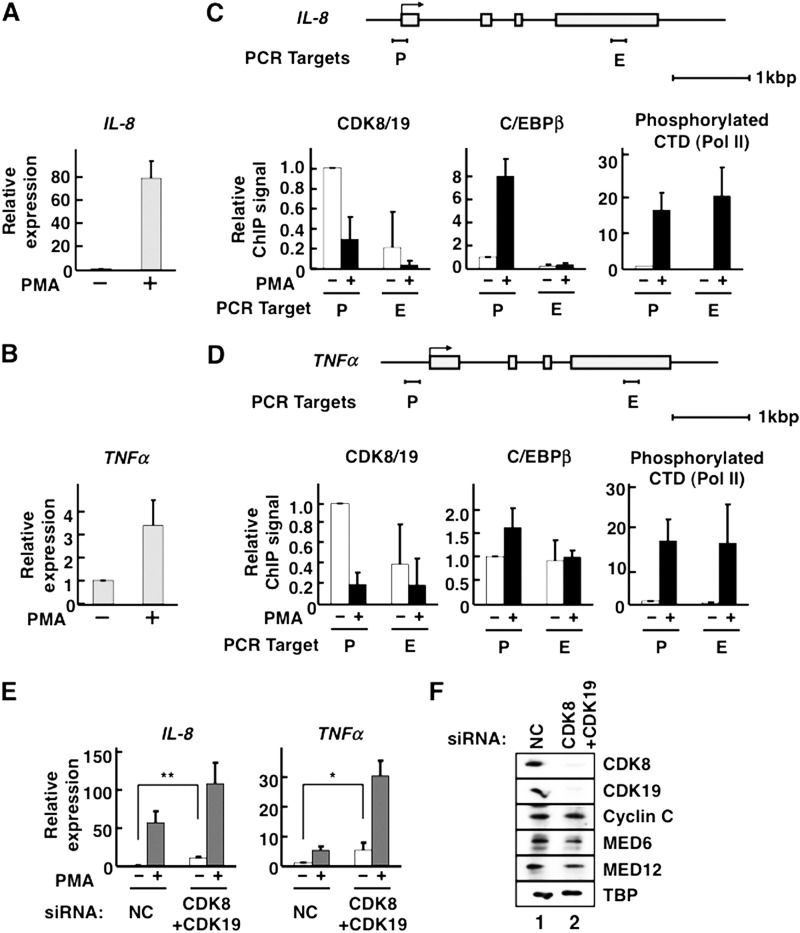
FIGURE 1.
Mediator CDKs repress C/EBPβ-inducible transcription. A–D, HeLa S3 cells were treated with 25 ng/ml of PMA for 2 h at 37 °C. A and B, qPCR for the measurement of IL-8 (A) or TNFα (B) mRNA (n = 2 in each case). C and D, occupancies of CDK8/19, C/EBPβ, and phosphorylated Pol II C-terminal domain (CTD) on IL-8 (C) and TNFα (D) genes. Schematic gene structures are displayed above the corresponding panels. Gray boxes indicate exons. P, promoter region; E, exonic region. The amount of each bound protein was measured by ChIP followed by qPCR. ChIP was individually carried out three times (n = 3). The data were normalized by defining the signal level without PMA treatment as 1. E, expression levels of IL-8 and TNFα genes were measured by qPCRs in CDK8/CDK19 double-knockdown cells treated with 25 ng/ml PMA for 2 h (n = 4). The data were normalized by defining the signal level without PMA treatment in the presence of nontarget control (NC) siRNA as 1. F, the effects of siRNA knockdown on protein expression of Mediator CDKs. After siRNA treatment, cell lysate proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. Mediator subunits and the general transcription factor TBP (as a control) were detected by Western blotting using antibodies against CDK8, CDK19, cyclin C, MED6, MED12, and TBP, as indicated on the right side. In all panels, the error bars show S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.