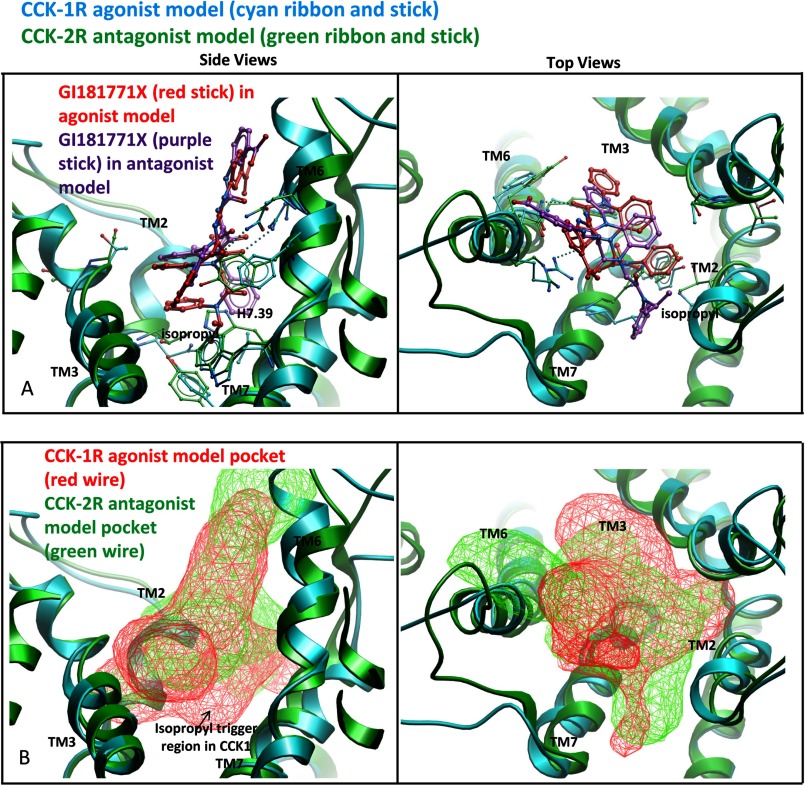
FIGURE 7.
Molecular basis for receptor subtype-selective activation of CCK receptors. Shown is a comparison of the predicted docking poses of GI181771X to the type 1 CCK receptor where it is an agonist (receptor in cyan ribbon, ligand in red stick) and to the type 2 CCK receptor where it is an antagonist (receptor in green ribbon, ligand in purple stick). The left viewpoint is from the side of the TM domains looking through TM4 and the right viewpoint is from the extracellular side with the loops cut away for clarity. In the upper pair of panel A, the ligand appears to be unable to make the same interactions in the type 2 CCK receptor that it makes in the type 1 CCK receptor, because His376 (7.39) blocks the binding of the isopropyl group. The isopropyl group was orientated toward residues 7.39 and 7.43 in the type 1 CCK receptor model (left) but toward the extracellular region in the type 2 CCK receptor model (right). We postulate that this steric hindrance prevents the isopropyl group from acting as a trigger in the type 2 CCK receptor. In the lower pair of panel B, the binding pocket for the agonist within the type 1 CCK receptor (red wire mesh) is compared with the binding pocket for the antagonist within the type 2 CCK receptor (green wire mesh). There is a lack of pocket volume in the isopropyl trigger region in the type 2 CCK receptor model.