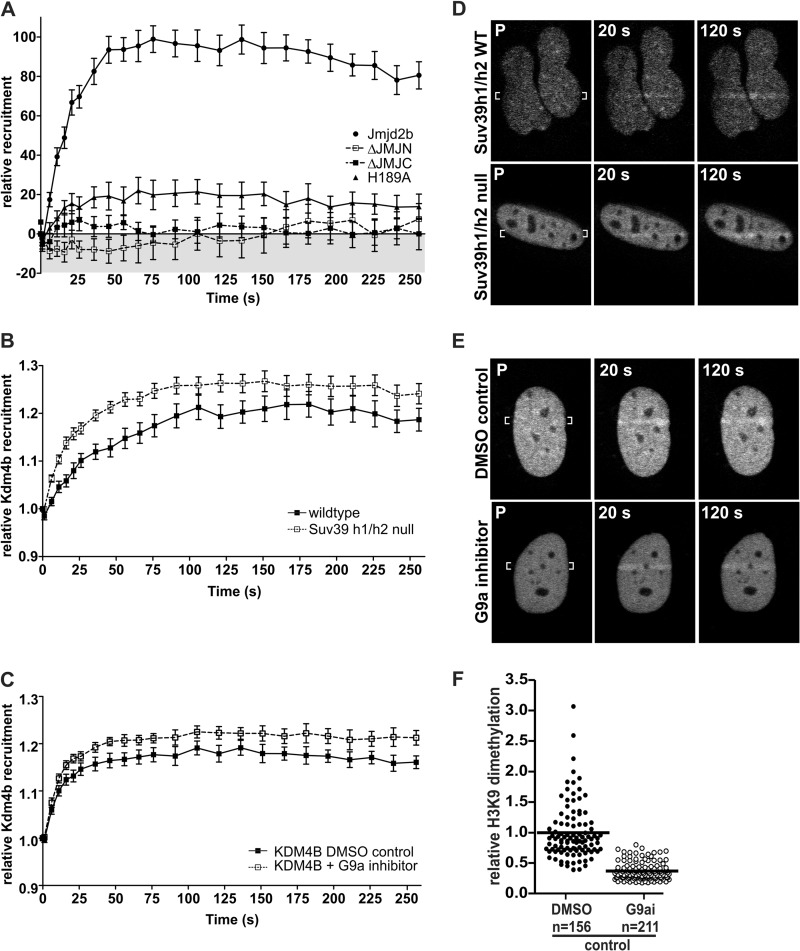
FIGURE 2.
The influence of demethylase activity on the recruitment of Kdm4b-EGFP to DNA damage. A, deletion of either the JmjN domain or the JmjC domain abolished Kdm4b-EGFP recruitment to the DNA damage tracks. Mutational inactivation of Kdm4b-EGFP (H189A mutation in the JmjC domain) resulted in at least an 80% reduction in recruitment. Graphs represent the mean values for at least 12 nuclei ± S.E. B and D, Kdm4b-EGFP recruited more readily to the DNA damage tracks in the Suv39H1/H3-double null MEFS (n = 25) than in the isogenic wild type control MEFs (n = 15). P, pre-irradiation. C and E, similarly, reduction of H3K9me2 levels through the inhibition of the G9a methyltransferase (n = 21) resulted in enhanced Kdm4b-EGFP recruitment to the DNA damage tracks, as compared with DMSO control cells (n = 18). F, shown is an example of the decreased H3K9me2 methylation observed after 3 days of treatment with 800 nm G9a inhibitor UNC0638. Mean decreases in H3K9me2 between experiments ranged from 60 to 70%.