Fig. 6.
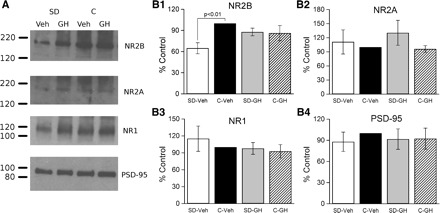
Hippocampal synaptic NMDAR subunit 2B (NR2B) expression was decreased after sleep deprivation but restored by GH injection. Proteins were isolated from synaptosomal membranes, separated by gel electrophoresis, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and probed using antibodies specific for NMDAR subunits (NR2B, NR2A, NR1) and the postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95). A: results from 1 replication of this experiment. Each replication included 4 animals, 1 from each group (SD-Veh, SD-GH, C-Veh, C-GH). In this replication, NR2B expression (top) was substantially reduced in SD-Veh animals, but was restored to control level by GH injection, whereas NR2A and NR1 subunits (middle rows) were less affected. Subunit expression did not differ between control groups (GH or Veh). There were no differences in PSD-95. B, 1–4: this experiment was repeated a total of 5 times (a total of 5 animals/treatment condition). Protein expression was quantified by film densitometry and normalized within each blot to C-Veh. Normalized values were averaged across blots (animals). The only consistent change in protein expression was for the NR2B subunit (B1), which was significantly reduced in the SD-Veh group compared with the C-Veh group, and that was restored by GH injection (no significant difference between SD-GH and C-GH). B, 2–4: there were no differences between the SD-Veh and C-Veh or SD-GH and C-GH groups for NR2A, NR1, and PSD-95.
