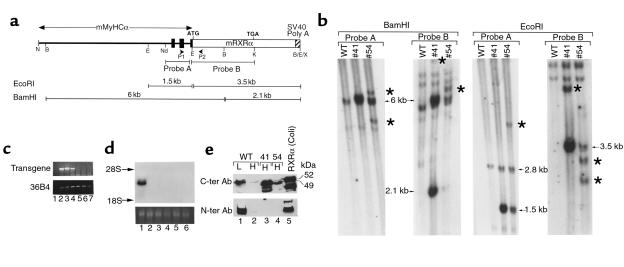
Figure 1.
Molecular characterization of MyHCα-RXRα transgenic mice. (a) Schematic representation of the transgene construct (not at scale). Black boxes indicate exons 1–3 of the MyHCα gene, which correspond to 5′-untranslated sequences. P1 and P2 are the RT-PCR primer used in the experiment shown in Figure 2a. Probe A corresponds to a EcoRI-NdeI fragment from the MyHCα gene, and probe B corresponds to a EcoRI-KpnI fragment containing all RXRα coding sequences. Fragments detected by these probes after EcoRI or BamHI digestion are shown. B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; K, KpnI; N, NotI; Nd, NdeI; X, XhoI. (b) Southern blot analysis. A total of 10 μg of BamHI- or EcoRI-restricted genomic DNA from WT mice or mice from lines 41 or 54 were analyzed by Southern blotting with probes A and probe B, as indicated. Arrows point to the bands of the expected size, whereas stars point to additional bands having undergone some deletions or rearrangements. (c) RT-PCR analysis of tissue samples from line 41. Lanes 1–7 correspond to: (1) adult ventricle with the reverse transcriptase omitted in the RT step, (2) adult ventricle, (3) adult atrium, (4) lungs, (5) skeletal muscle, (6) liver, and (7) brain. The top panel corresponds to transgene transcript amplification with the transgene-specific primers depicted in a; the bottom panel corresponds to the control amplification of 36B4 gene transcripts (39). (d) Northern blot analysis of transgene expression in line 41. A total of 20 μg of total RNA from adult heart (lane 1), lungs (lane 2), spleen (lane 3), skeletal muscle (lane 4), kidney (lane 5), and liver (lane 6) were analyzed by Northern blotting with a cDNA probe corresponding to a 2-kb fragment containing the RXRα coding sequences. The bottom panel corresponds to the ethidium bromide staining of ribosomal 28S RNA of the same RNA sample separated on an identical gel. (e) Western blot analysis. A total of 50 μg of nuclear extracts prepared from WT liver (L) or heart (H) and from heart from transgenic mice from lines 41 or 54, as well as a control extract of bacterially produced RXRα (lane 5), was separated on a 8% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and revealed with polyclonal antibodies directed against either COOH-terminal RXRα epitopes (top panel) or an NH2-terminal RXRα epitope (bottom panel). Note that transgenic hearts express an RXRα polypeptide that is smaller than WT RXRα and not detected by the NH2-terminal antibody. Smaller fragments seen in lanes 3 and 5 likely correspond to proteolytic degradation products.