Fig. 7.
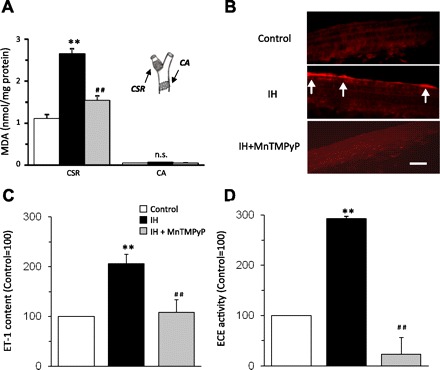
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate upregulation of ET-1 in the carotid sinus region by IH. A: malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, an index of ROS, were determined in the carotid sinus region (CSR) and common carotid artery (CA). IH increased ROS levels in the CSR but not in the CA, and this response was prevented by MnTMPyP, an antioxidant. Inset: the CSR and CA regions from which the data were derived. B: IH increased ET-1-like immunoreactivity in the carotid sinus region, and MnTMPyP treatment abolished this response. The scale bar represents 10 μm. C and D: MnTMPyP prevents the effects of IH on ET-1 (C) and ECE activity in the carotid sinus region (D). Data are means ± SE from control and IH-treated rats (n = 6 in each group). **Significant difference compared with control tissues (P < 0.01). ##Significant difference compared with IH-treated tissues (P < 0.01).
