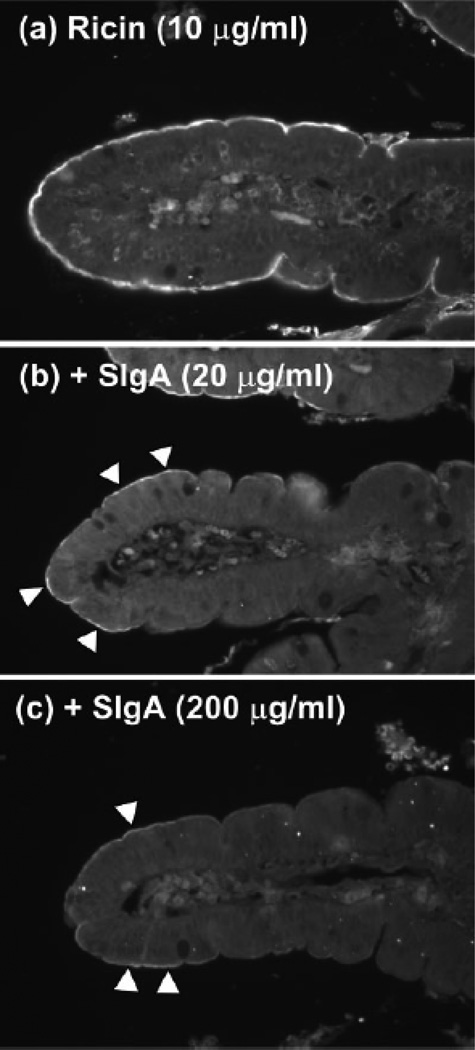
Fig. 2. SIgA competitively inhibits ricin toxin binding to the luminal surfaces of human intestinal villi.
Biotinylated ricin (10 µg/ml) was incubated for 1 h with PBS (a) or indicated concentrations of sIgA (b and c), and then applied to deparaffinized tissue sections of human duodenum. Sections were then labeled with streptavidin-FITC and visualized by fluorescence microscopy. a, Ricin labeled the luminal aspects of intestinal villi strongly and uniformly. Ricin also weakly labeled cells within the lamina propria. B and c, Preincubation of ricin with indicated concentrations of sIgA Abs reduced toxin attachment to luminal aspects of the intestinal villi. Arrowheads highlight areas of visible toxin labeling. Figure reproduced from (Mantis et al., 2004) with permission from the American Association of Immunologists.