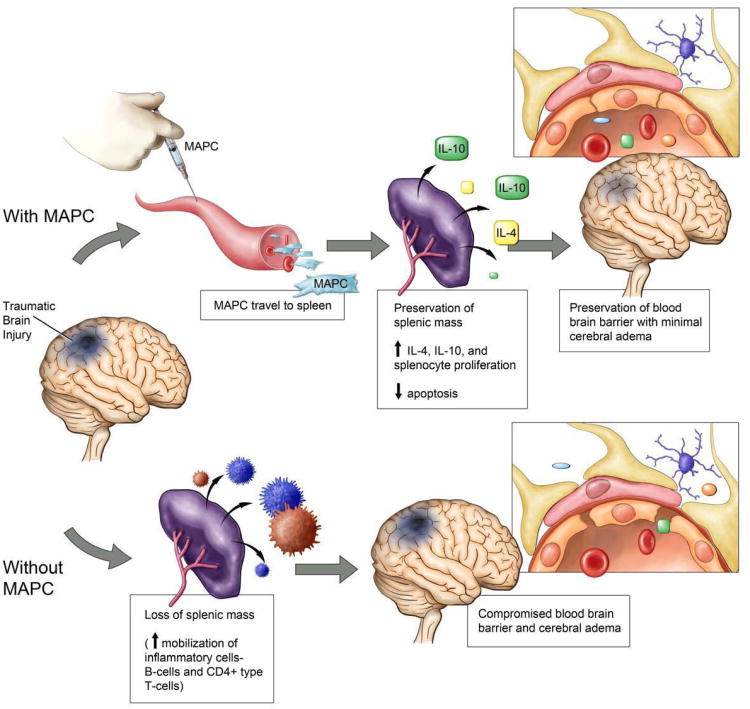
Figure 11.
Mechanism of neurovascular protection after the intravenous injection of MAPC. Our data show that CCI injury results in a decreased splenic mass and an increase in BBB permeability. Intravenous MAPC therapy preserved splenic mass and returned BBB permeability towards sham levels at both cell dosages. MAPC therapy leads to an increase in CD4+ splenocyte proliferation thereby increasing the production of anti inflammatory cytokines. The observed modulation of the inflammatory response causes stabilization of the cerebral microvasculature leading to the preservation of the BBB.