Fig. 4.
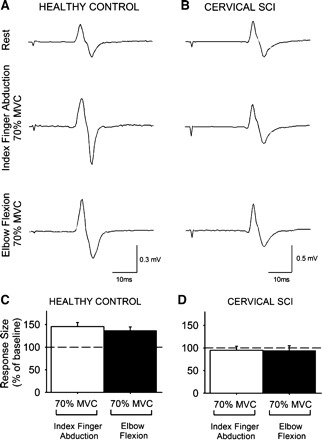
Cervicomedullary motor evoked potentials (CMEPs). A and B: CMEPs recorded from the resting FDI of a healthy control subject (A) and a patient with cervical SCI (B) while the other side remained at rest or performed 70% of MVC during index finger abduction or elbow flexion. C and D: x-axis shows the conditions tested (70% of MVC during index finger abduction, white bars; 70% of MVC during elbow flexion, black bars), and y-axis shows the size of the FDI CMEP as % of the baseline FDI CMEP. Note the increase in FDI MEP size during contralateral index finger abduction and elbow flexion in the healthy control subject (C) but not in the patient with cervical SCI (D). Error bars indicate SE.
