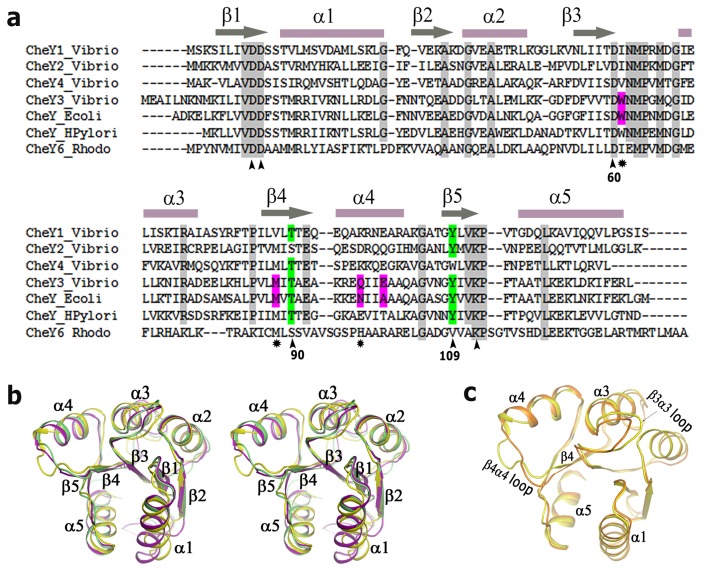
Figure 1. Sequence alignment and overall structure comparison of CheYs.
(a) Amino acid sequences of VcCheY1–VcCheY4 are aligned with CheY6 of Rhodobacter spaeroides, CheY of Escherichia coli and CheY1 of Helicobacter pylori. Secondary structural elements are marked and labelled at the top. At the bottom important conserved residues implicated in activation/metal binding are marked as (∧) whereas other important residues are indicated as (*); as EcChey and StCheY possess 99% sequence identity only EcCheY was shown in the alignment file. (b) Stereo representation showing the comparison of the overall structures of VcCheY3 (violet), StCheY (green), each in free state, with VcCheY4free (yellow); (c) Superposition of the overall structure of VcCheY4free (yellow) on VcCheY4sulf (orange) showing the significant differences in helix α4 and β4α4 loop.