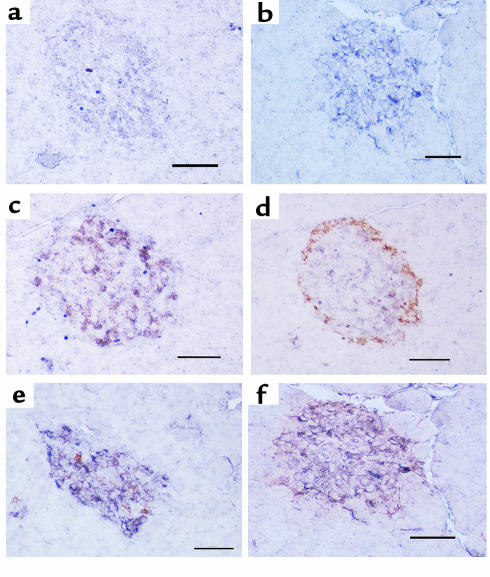
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemistry (alkaline phosphatase method with NBT/BCIP colorization) for PC1 (1/50 dilution) in pancreata from vehicle-treated (a) or STZ-treated (b) rats and double immunohistochemistry staining for PC1 (1/50 dilution) (alkaline phosphatase method with NBT/BCIP colorization; purple) and insulin (10 μg/mL) (peroxidase method with DAB colorization; rust) (c and e) or glucagon (1/75 dilution) (peroxidase method with DAB colorization; rust) in pancreata from vehicle-treated (c and d) or STZ-treated (e and f) rats. PC1 was much more intense in diabetic islets (b) than in control islets (a) and was mainly colocalized with insulin-producing cells (c) but occasionally with glucagon-producing cells (d) in control islets. On the other hand, PC1 immunoreactivity was observed in both insulin-producing cells (e) and glucagon-producing cells (f) in diabetic islets. The increase in PC1 immunoreactivity appears confined to the glucagon-staining cells. Scale bar = 50 μm; 4 animals per group.