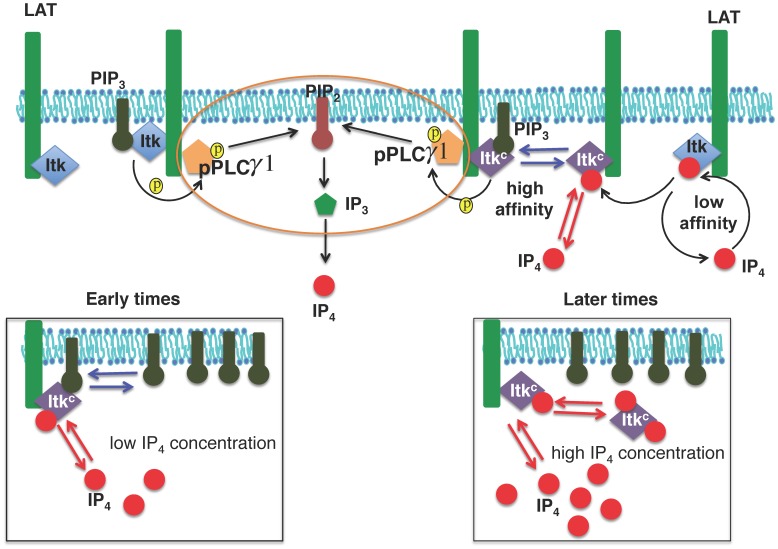
Figure 1. Relevant basic interactions between Itk, PIP3 and IP4.
Following TCR-pMHC binding, Itk molecules are bound by the LAT signalosome via SLP-76 (not shown). Itk molecules (monomers or dimers, blue diamonds), bind the membrane lipid PIP3 with low affinity through their PH domains. PIP3 bound Itk phosphorylates and thereby activates LAT-bound PLCγ1. Activated PLCγ1 then hydrolyzes the membrane lipid PIP2 into the soluble second messenger IP3, a key mediator of Ca2+ mobilization. IP3 3-kinase B (ItpkB) converts IP3 into IP4 (red filled circle). For our in silico models, we simplified this series of reactions, encircled by the orange oval, into a single second order reaction where PIP3 bound Itk converts PIP2 into IP4. In models M1–M4 and M7, IP4 modifies the Itk PH domain (denoted as ItkC, purple diamonds) to promote PIP3 and IP4 binding to the Itk PH domain. At the onset of the signaling, when the concentration of IP4 is smaller than that of PIP3, IP4 helps ItkC to bind to PIP3 (left lower panel). However, as the concentration of IP4 is increased at later times, IP4 outcompetes PIP3 for binding to ItkC and sequesters ItkC to the cytosol (right lower panel). In models M5/M6, IP4 and PIP3 do not augment each other’s binding to Itk. However, IP4 still outcompetes PIP3 for Itk PH domain binding when the number of IP4 molecules becomes much larger than that of PIP3 molecules at later times.