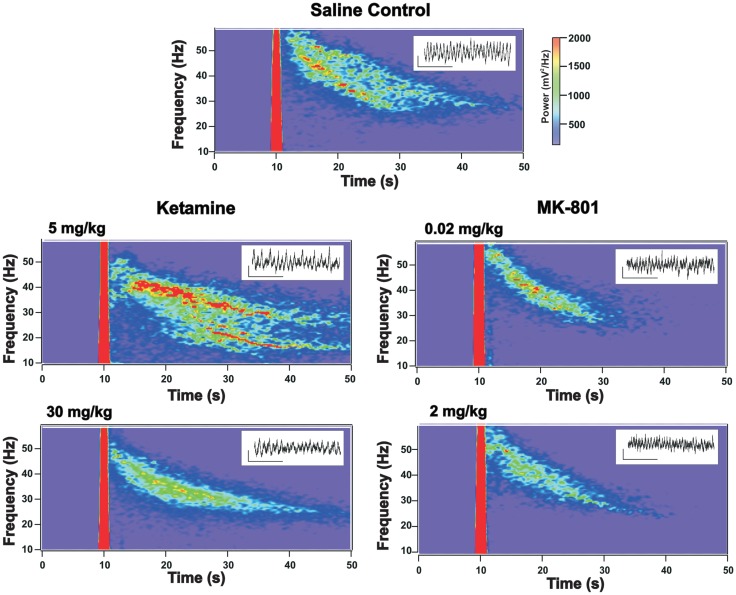
Figure 1.
Grand average of kainate (KA) elicited oscillatory response in prelimbic cortex (PrL) slices prepared from mice receiving chronic administration of NMDAR antagonists. Time-frequency spectrograms show the average KA-elicited oscillatory response from acute PrL slices obtained from mice receiving chronic injections of saline (control), ketamine (5 and 30 mg/kg), or MK-801 (0.02 and 2 mg/kg). Note: the mechanical transient associated with KA application appears as a thick red line due to oversaturation. Compared to saline treated controls, the elicited response in slices from mice chronically treated with 30 mg/kg ketamine shows a reduction in the peak frequency (see Figure 2) and in the power in the (40–50 Hz) band, which is almost absent in slices from drug treated mice 5–10 s following KA application. 5 mg/kg ketamine treatment also appears to show a slight decrease in the higher-frequency elicited response, while the response at lower frequency bands appears elevated (not significant). MK-801 treated mice show a trend toward reduced power but no change in peak frequency (see Figure 2 and text). Insets provide representative examples of GBO signal traces recorded from acute slices from mice in each treatment group (scale bar for insets: x = 200 ms, y = 50 μV).