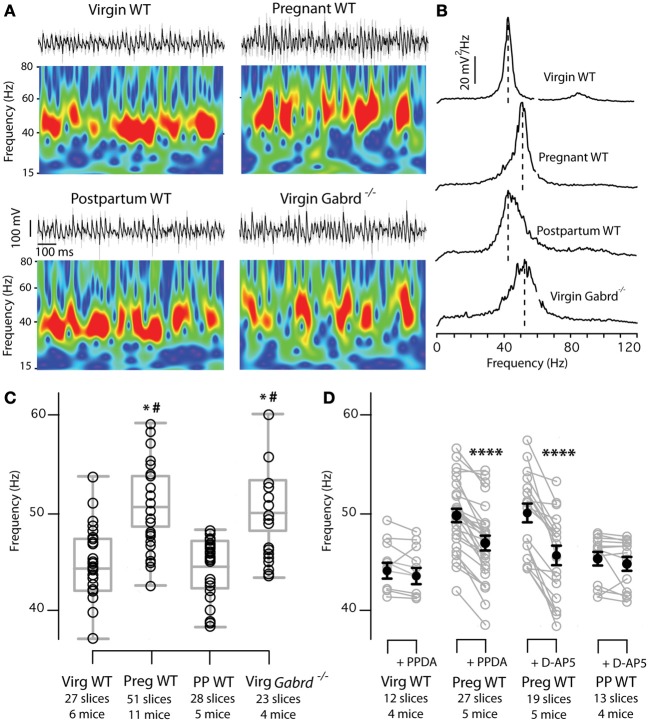
Figure 6.
γ Oscillations frequency is increased in the CA3 of pregnant animals in the absence of physiological ALLO levels. Increased CA3 γ oscillations frequency in slices of WT pregnant mice is sustained by NMDA-Rs activation on interneurons. (A) Kainate induced γ oscillations (50 nM) recorded extracellularly in CA3 stratum pyramidale at different gestational states show higher frequency in slices of WT pregnant and Gabrd−/− virgin mice compared to slices from WT virgin and postpartum mice. Upper traces: representative 1 s epochs of LFPs band-pass filtered between 15 and 120 Hz (black) and raw traces (gray). Morlet wavelet transforms of the corresponding traces show γ oscillatory behavior. Warmer colors represent higher power, and the same scale has been used for all four wavelets. (B) Plots of power spectral density calculated over 180 s periods of the same recordings as in (A). Note increased γ frequency in slices from pregnant and Gabrd−/− mice. No differences are found in power at peak frequency or total power (30–120 Hz) (C), Box plots showing peak frequencies for the four experimental groups. Each dot symbolizes the peak frequency of one slice calculated as the frequency with the highest power in a 180 s period power spectral density as in (B). Box plots represent mean, 25th and 75th percentile, and largest and smallest values. Significance established by One-Way ANOVA followed by Turkey's multiple comparisons test. *p < 0.0001 between WT pregnant and WT virgin or WT postpartum respectively. #p < 0.0001 between Gabrd−/− virgin and WT virgin or WT postpartum respectively. (D) In slices of WT pregnant mice bath application of the NMDA-R subunit-unspecific antagonists D-AP5 (25 μ M) or GluN2D-containing NMDA-Rs specific antagonist PPDA (1μ M) decreases γ oscillations frequency to WT virgin and WT postpartum (PP) values. The same drugs have no effect on γ frequencies of slices of WT virgin or WT postpartum mice. Mean frequency ± SEM in Hz, significance established by two-tailed paired t-test: pregnant PPDA = 49.7 ± 0.7 to 46.9 ± 0.7, p < 0.0001, n = 27 slices, 5 mice; virgin PPDA = 44.0 ± 0.8 to 43.5 ± 0.9 p = 0.1, n = 12 slices, 4 mice; pregnant D-AP5 = 49.8 ± 0.96 to 45.6 ± 1.0 p < 0.0001, n = 19 slices, 5 mice; postpartum D-AP5 = 45. 5 ± 0.68 to 45.1 ± 0.68 p = 0.2, n = 13 slices, 4 mice. Asterisks denote significance. n's for each group are reported in the figure.