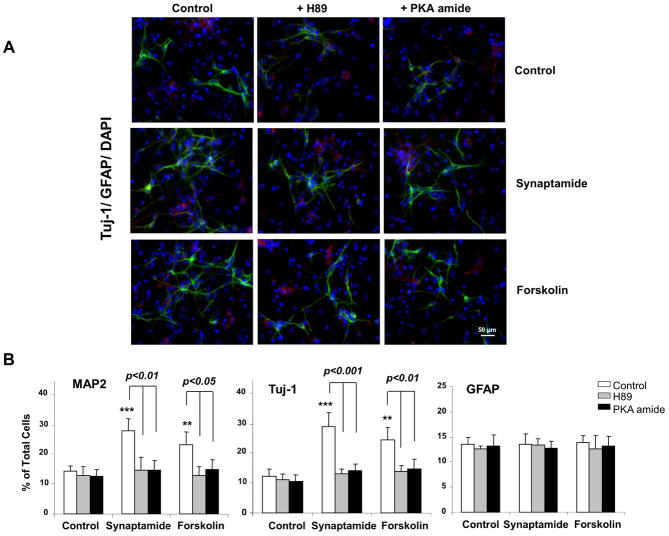
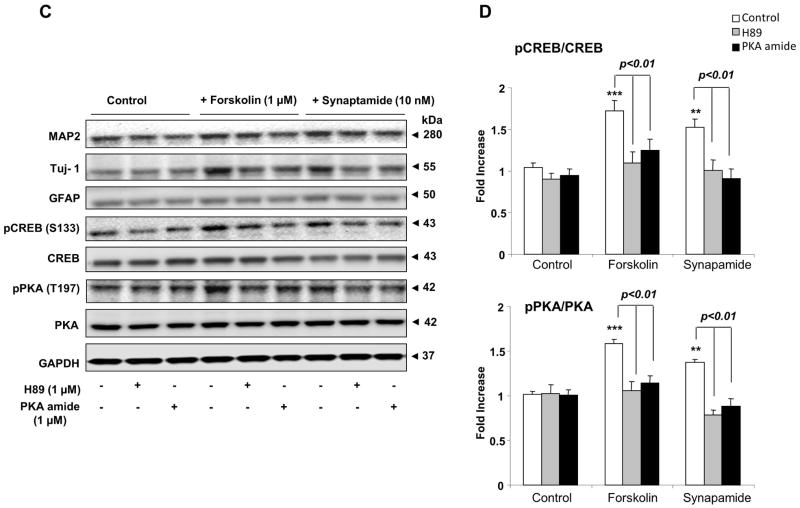
Figure 4.
Critical role of PKA/CREB activation in synaptamide-induced neuronal differentiation of NSCs. NSCs were treated with PKA inhibitor, H89 (1 μM) or PKA inhibitor 6–22 amide (1 μM) for 30 min, and then incubated with synaptamide (10 nM) or forskolin (1 μM) for 7 days. NSCs cells were stained for Tuj-1 (green), GFAP (red) and nuclei (DAPI), and visualized by fluorescence microscopy (A), and the percentage of Tuj-1 and GFAP positive cells was evaluated using MetaMorph software (B). Western blot analysis was performed for CREB and PKA phosphorylation along with MAP2, Tuj-1 and GFAP (C). Phosphorylated CREB and PKA level was normalized to the total CREB and total PKA, respectively, and compared to their basal levels (D). Micrographs for MAP2 staining are not shown. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD of triplicates, representing three independent experiments. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001 compared to DMSO control.