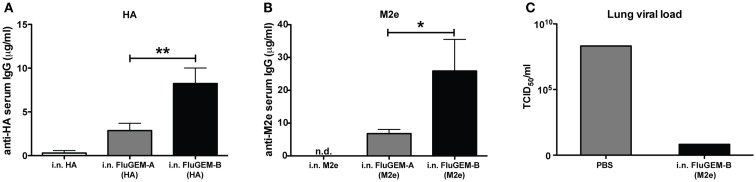
Figure 5.
Immune responses induced upon i.n. vaccination with FluGEM-A and FluGEM-B. Groups of 10 mice were vaccinated i.n. with HA- or M2e-based FluGEM-A or FluGEM-B. Vaccination dose in the case of HA-based vaccines (A) was 1 μg HA mixed with or bound to 0.3 mg BLP. Animals received in total three doses (day 0, 10, and 20) and were sacrificed 2 weeks after the final immunization (day 34). Vaccination dose in the case of M2e-based vaccines (B) was 6 μg M2e equivalent mixed with or bound to 0.38 mg BLPs. Animals received in total three doses (day 0, 21, and 42) and were sacrificed 3 weeks after the final immunization (day 63). In both cases physical coupling of the antigen (FluGEM-B) induced a significant increase in serum IgG titers. *p < 0.05; **0.01; one-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (n = 10). (C) Mice (n = 3) were vaccinated three times (day 0, 21, and 42) i.n. with M2e-based FluGEM-B vaccine containing 50 μg M2e and 0.3 mg BLPs. Three weeks after the final immunization mice were exposed to challenge with 4LD50 × 47 (H3N2) influenza virus. Animals were sacrificed 6 days post-challenge and virus titers were evaluated as a protection parameter. In lungs of all infected mice vaccinated i.n. with M2e-based FluGEM-B decrease of viral load was observed, which indicates protection capacity of the FluGEM-B vaccine.