Fig. 2.
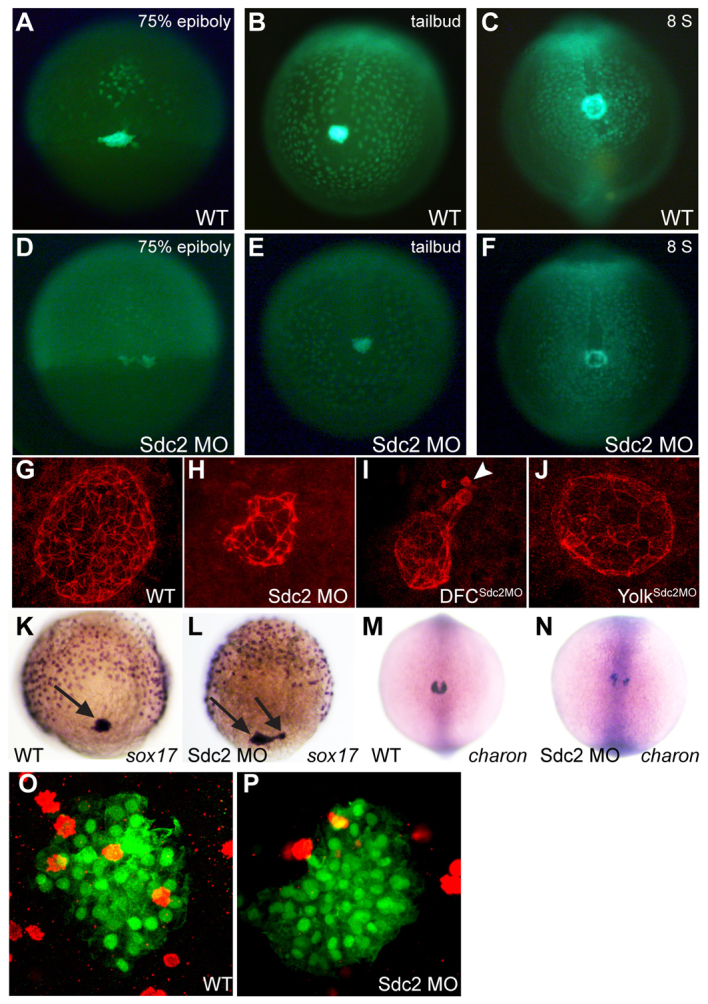
Cell-autonomous regulation of KV morphogenesis by Sdc2. (A-F) Comparison of time-lapse images of uninjected (A-C) and sdc2 morphant (D-F) Tg(sox17:GFP) zebrafish embryos illustrates defective DFC coalescence and KV morphogenesis in sdc2 morphants. KV morphology and size were affected by variation in DFC number and coalescence. (G-J) Anti-ζPKC antibody labels the apical surface of KV cells lining the KV lumen. At the 8-somite stage (SS), KV morphology was normal in wild-type (G) and yolksdc2MO (J) embryos. By contrast, global sdc2 morphants (H) and DFCsdc2MO embryos (I) displayed abnormalities in KV shape as well as incomplete DFC incorporation into the main KV, resulting in aberrant secondary ‘mini vesicles’ (arrowhead in I). (K,L) sox17 expression at 80-90% epiboly reveals tightly clustered DFCs (arrows) in wild-type embryos (K) but loosely adherent DFCs in sdc2 morphants (L). (M,N) Expression of charon is perturbed in sdc2 morphants, indicating KV disorganization. (O,P) pH3 staining in DFCs of wild type [Tg(sox17:GFP)s870] and sdc2 morphants at tailbud to 2-somite stage (see also Table 1).
