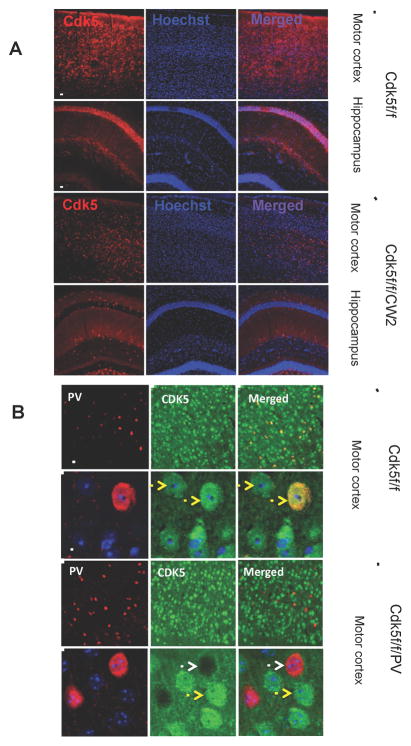
Figure 1. Conditional deletion of Cdk5 in excitatory neurons of the forebrain.
(A) Immunocytochemistry conducted using the Cdk5 antibody on Cdk5f/f (control) and Cdk5f/f/CW2 (Cdk5 conditional knockout) animals revealed dramatically reduced Cdk5 signal in the motor cortex and hippocampus of Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals (Scale bars, 100 μm).
(B) Positive and negative controls for CDK5 ablation in the cortical neurons. The images represent anti-CDK5 staining in the cortices of the fCdk5 mice and the littermate Cdk5f/f/PV-Cre mice in which CDK5 was ablated specifically in PV-neurons. Note that all the PV+ neurons are CDK5− while the all the other neurons show CDK5 immunoreactivity. Antibody used the immonostaining are the same anti-Cdk5 used for analysis of Cdk5f/f/CW2 mouse brains (rabbit C-8; Santa Cruz Biotech). Yellow arrows: wild type neurons expressing Cdk5; White arrows: the neurons with Cdk5 ablated. Scale bars, 15 μm.