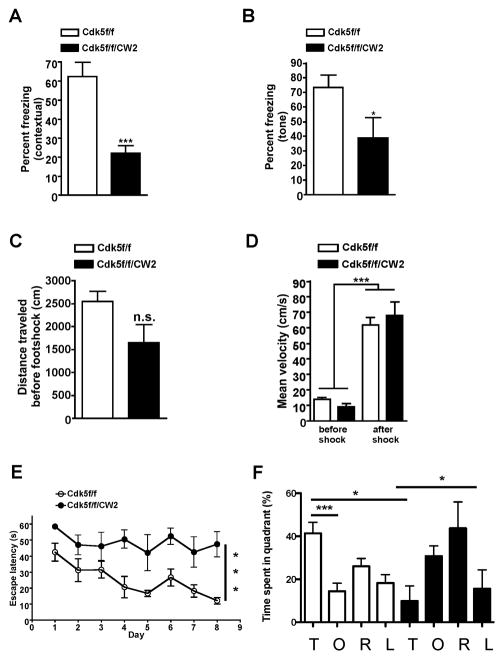
Figure 4. Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals are severely impaired in hippocampus-dependent cognitive tasks.
(A) Whereas control Cdk5f/f littermates displayed robust freezing levels upon testing 24 hr after the footshock, Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals were significantly impaired in contextual fear memory (Cdk5f/f, 62.35 ± 7.452; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 22.22 ± 3.928; p=0.0004).
(B) Compared to control Cdk5f/f littermates, tone-dependent fear conditioning was also significantly impaired in Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals (Cdk5f/f, 73.46 ± 8.475; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 38.89 ± 14.05, p=0.0471). N=9 for Cdk5f/f; N=8 for Cdk5f/f/CW2. Data shown are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using One-way ANOVA or Student’s t-test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).
(C) The distance traveled in the fear conditioning chamber did not significant differ between control Cdk5f/f and Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals in the 3 min exploration time before the footshock (Cdk5f/f, 2551 ± 216.5; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 1648 ± 393.9; p=0.0558).
(D) Both Cdk5f/f and Cdk5f/f/CW2 groups responded to the footshock as shown by their increase in mean velocity before (left) and after (right) the shock. Before footshock: Cdk5f/f, 14.17 ± 1.203; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 9.155 ± 2.188. After footshock: Cdk5f/f, 61.91 ± 4.897; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 68.00 ± 8.888.
(E) While control Cdk5f/f animals learned the spatial memory task during the 8 day training session as demonstrated by a decrease in the escape latency, Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals were consistently impaired in acquisition of the spatial memory during the training session (Escape latency on the last day of training: 12.15 +/− 2.06 s for Cdk5f/f versus 47 +/− 7.8 s for Cdk5f/f/CW2; p<0.0005 for control versus mutant groups).
(F) During the probe trial on day 9, control Cdk5f/f mice spent more time searching for the platform in the target (T) quadrant (41.3 +/− 5%; p<0.001 for the target quadrant), while Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals spent significantly less time in the target (T) quadrant (9.8 +/− 7%) and instead spent more time searching for the platform in the opposite (O) quadrant (30.78 +/− 4.7%) and the quadrant to the right (R) (43.7 +/− 12.2) of the target quadrant. N=8 for Cdk5f/f; N=5 for Cdk5f/f/CW2. Data shown are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using One-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).