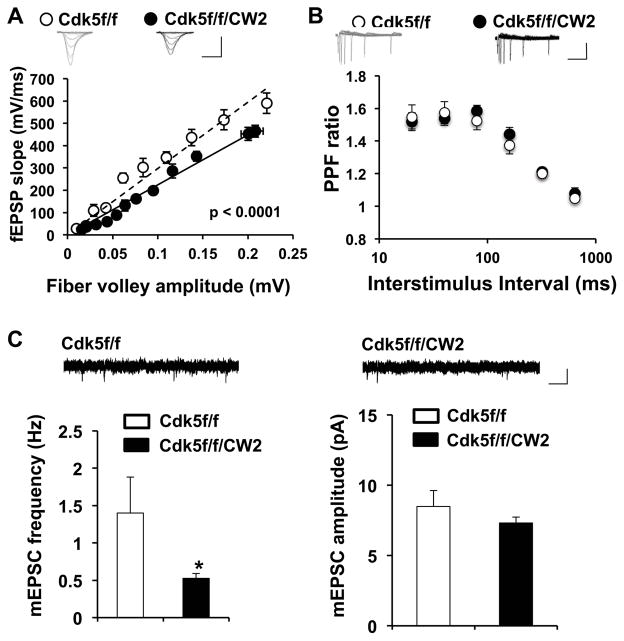
Figure 5. Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals exhibit deficits in synaptic transmission.
(A) Basal synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral pathway is severely impaired in acute hippocampal slices prepared from Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals compared to those obtained from control Cdk5f/f animals. The data was fit by linear regression, which were determined to be significantly different by ANOVA with respect to slope (p<0.0001). Scale bars, 0.4 mV, 4 ms.
(B) Compared to slices prepared from control Cdk5f/f animals, the paired-pulse facilitation ratios at various interstimulus intervals are not significantly different from slices from Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals. Scale bars, 0.2 mV, 100 ms.
(C) Compared to slices prepared from control Cdk5f/f animals, the frequency of mEPSC is significantly decreased in slices prepared from Cdk5f/f/CW2 animals (Cdk5f/f, 1.40 ± 0.48; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 0.53 ± 0.06; p = 0.04). The mEPSC amplitude did not significantly differ between the control Cdk5f/f and Cdk5f/f/CW2 groups (Cdk5f/f, 8.49 ± 1.15; Cdk5f/f/CW2, 7.31 ± 0.42; p = 0.289). N=3 animals, 9–13 slices, for both Cdk5f/f and Cdk5f/f/CW2 genotypes. Scale bars, 10 pA, 50 ms. Data shown are means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using Student’s t-test or ANOVA (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).