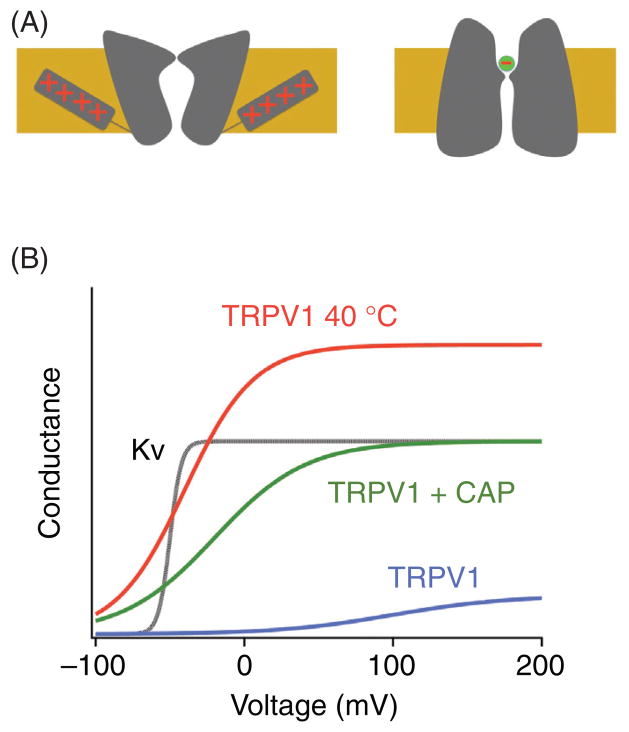
Figure 4.
(A) schematic drawing of the voltage-dependent gating of the Kv channel (left) and CLC-0 channel (right). The red + and − signs indicate positive charged amino acids and chloride ion, respectively. For the Kv channel, charges carried by arginine and lysine residues in the fourth transmembrane segment, S4, serve as the primary gating charges. Changes in transmembrane voltage drive the movement of S4, which is coupled to the opening of the activation gate. For the CLC-0 channel, the permeant ion Cl− in the pore carries the gating charge. (B) Voltage-dependent gating of TRPV1 and Kv channels.