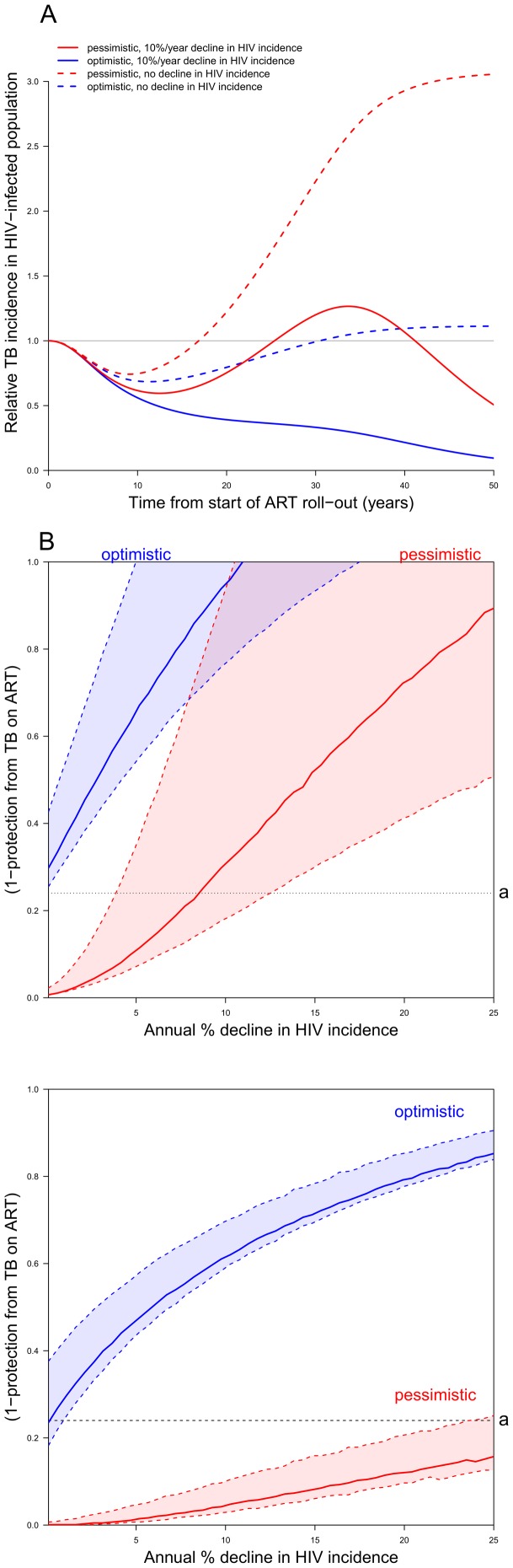
Figure 2. Results from the model. A. TB incidence dynamics.
Annual population-level TB incidence among HIV-infected persons relative to the value before ART scale up. ART coverage, with initiation at CD4 count of 225 cells per microliter, is assumed to increase from 0% to 100% over 5-years. Blue and red lines correspond to the pessimistic and optimistic scenarios of Figures 1B & C. Dashed lines assume no drop in HIV incidence; solid lines correspond to an HIV incidence declining at a proportional rate of 10% per year. B. Contours separating regions where cumulative TB incidence over 50 years is increased from regions where it is decreased, as the level of protection against TB conferred by ART (IRR) and the decline in HIV incidence vary. The solid colored lines correspond to the default dependence of life expectancy on CD4 count at ART initiation (i.e. p = 0.5, see main text). Regions below these lines correspond to decreases in cumulative incidence; above the lines to increases. Red and blue lines correspond to the optimistic and pessimistic scenarios as shown in Figures 1B & C and described in the text. The shaded regions bounded by dashed lines indicate the variation of the contours of zero change for cumulative incidence as the dependency of life expectancy on CD4 count at ART initiation is varied (p ranging from 0.25 to 1). Contours sweep from the lower dashed line for longer life expectancies to the upper dashed line at shorter life expectancies. The horizontal black dotted line represents the level of protection after CD4 recovery corresponding to Figures 1B & C, i.e. to a = 0.24 for those started at CD4A = 225 cells per microliter. C. Contours separating regions where peak TB incidence over 50 years is higher than baseline from regions where it is lower, as the level of protection against TB conferred by ART (IRR) and the decline in HIV incidence vary. The conditions and interpretation are as for Figure 2B, but with the outcome being peak rather than cumulative TB incidence over 50 years: the areas below the lines correspond to situations where the peak incidence does not exceed baseline.