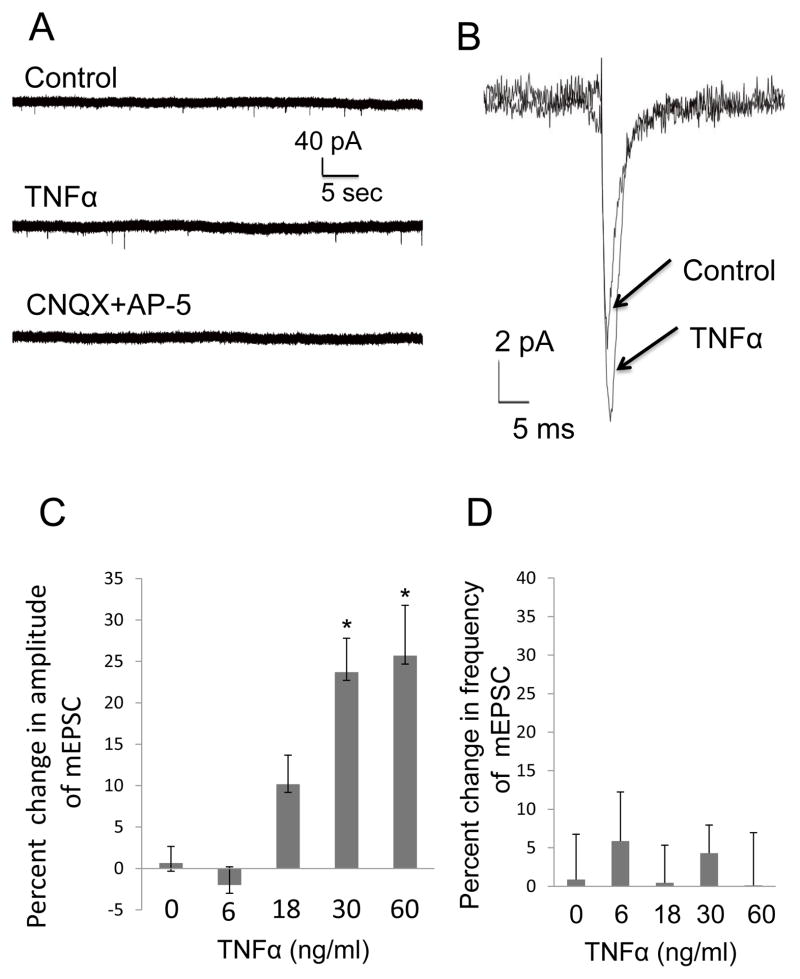
Figure 1. TNFα increased the Amplitude of mEPSCs in CeA.
(A) Representative mEPSC recordings from the same neuron in the presence of 20 μM bicuculline (Control), and after TNFα (TNFα). Application of glutamate antagonists to that neuron (CNQX + AP-5) blocked the mEPSCs. The glutamate antagonist treatment completely blocked the mEPSCs in other neurons (n=5). (B) Averaged traces of mEPSCs from the same neuron in Fig. 1A prior (control) and in the presence of TNFα (60 ng/ml) showing the increase in mEPSC amplitude induced by TNFα (TNFα). (C) TNFα concentration enhanced the amplitude of mEPSCs concentration-dependently (n=5–8 for individual concentrations; F (4,24) = 12.30, p<0.0001) with a significant linear trend; r(29)=0.74, p<0.05. (D) TNFα did not to influence the frequency of mEPSCs [F (4,26)=0.22; p>0.05; n=5–8].