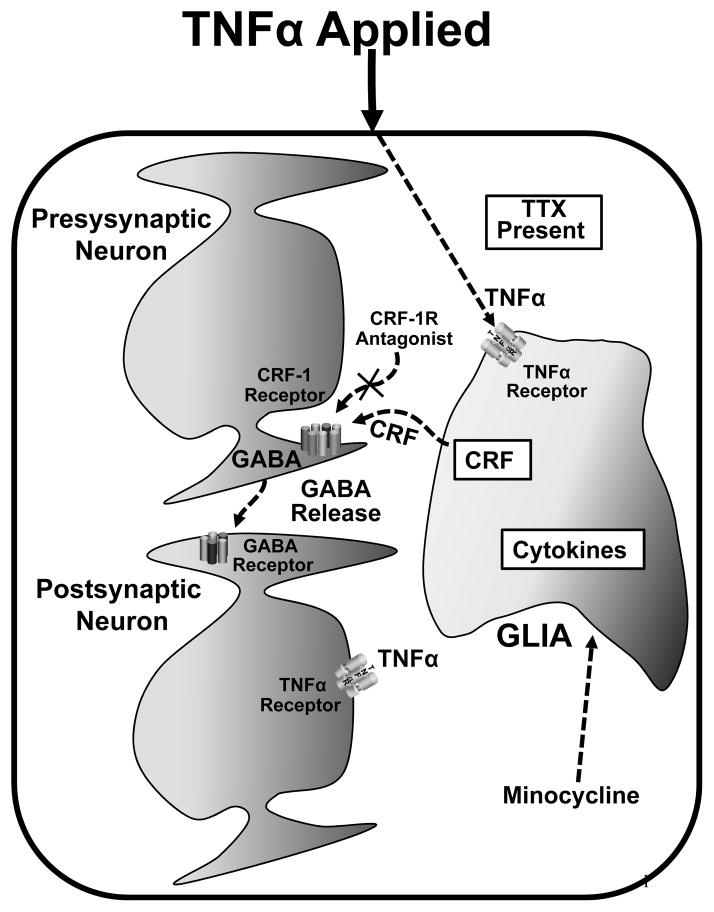
Fig. 8. Possible mechanism of TNFα-induced-CRF-dependent GABA release.
As noted, TNFα could act on a glial cell to induce glial release of CRF. This is consistent with the TNFα-induced release of GABA being blocked either by blocking glial activation with minocycline or by blocking the effect of CRF at its receptor on the presynaptic terminal with a CRF-1-antagonist [X]. Noted is that TNFα also acts on the post-synaptic neuron to activate the PI-3-K to allow amplitude of mEPSCs to be increased (Fig. 3)