Figure 1.
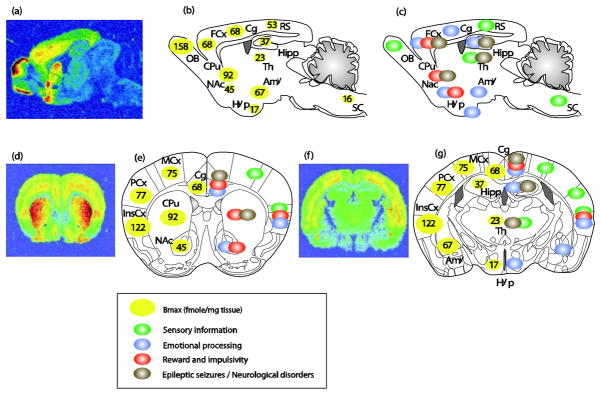
Anatomical distribution of delta opioid receptors and relevant brain functions. Top panels, sagittal sections; bottom panels, coronal sections at 2 different anterio-posterior positions ((e) bregma 0.98mm; (g) bregma −1.46mm). (a, d and f) ([3H]deltorphin ligand autoradiography reveals delta opioid receptor binding sites (courtesy of Ian Kitchen). (b, e left part and g left part) Quantification of DOR expression levels in fmole/mg of tissue (means from (Kitchen et al., 1997; Simonin et al., 1998; Slowe et al., 1999; Goody et al., 2002). DORs are particularly abundant in the OB, cortical regions (FCx, Cg, MCx, PCx and InsCx), amygdala and striatum (CPu and NAc). DORs are also expressed at moderate levels in the Hipp, RS, and at much lower level in Hyp, Th and SC. (c, e right part and g right part) Schematic representation of potential neural sites for DOR function. DORs are expressed in sensory regions (green circles), brain areas important for the regulation of anxiety and depression (blue circles adapted from (File et al., 2000; LeDoux, 2000; Cardinal et al., 2002; B. J. Everitt et al., 2003; Paulus & Stein, 2006; Rodrigues et al., 2009; Etkin et al., 2011; Gross & Canteras, 2012; Steenland et al., 2012)), brain sites for reward processing and inhibitory controls (red circles adapted from (Robbins & Everitt, 1996; Balleine & Dickinson, 1998; Kesner & Gilbert, 2007; Paton & Louie, 2012; Richard et al., 2012)) and areas relevant to epileptic seizures (grey circles adapted from (Andre et al., 1998; Brevard et al., 2006)). Abbreviations: Amy, Amygdala; Cg, Cingulate cortex; Cpu, Caudate Putamen; FCx, Frontal cortex; Hipp, Hippocampus; Hyp, Hypothalamus; InsCx, Insular cortex; MCx, Motor cortex; NAc, Nucleus Accumbens; OB, Olfactory Bulb; PCx, Parietal cortex; RS, Retrosplenial; SC, Spinal Cord; Th, Thalamus.
