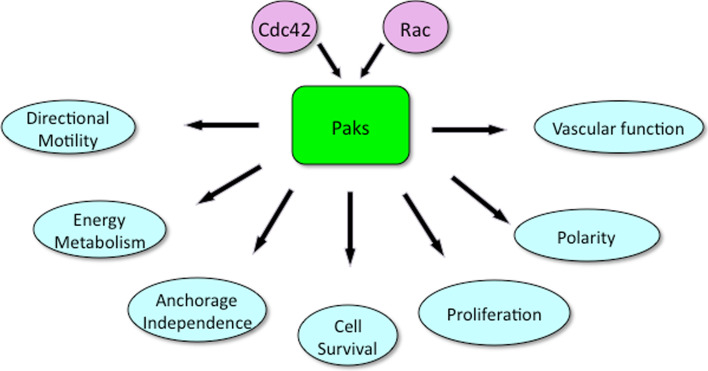
Fig. 1.
Cellular functions of Pak. Paks are activated by the small GTPases Cdc42 and Rac. Paks in turn activate signaling pathways that regulate a plethora of cellular events. In many but not all cases, activation is due to phosphorylation of protein substrates by Pak. The processes affected by Pak include directional motility and cell polarity (via phosphorylation of GEFs, GAPs, LIM kinase, Filamin A, p41Arc, etc.), energy metabolism (via phosphorylation of phosphoglucomutase 1 and perhaps other metabolic enzymes), cell survival (via activation of pro-survival proteins such as Akt and inactivation of BAD), cell proliferation (via phosphorylation of c-Raf and Mek1, as well as other growth-responsive signaling proteins), and vascular function (via phosphorylation of VE-cadherin)