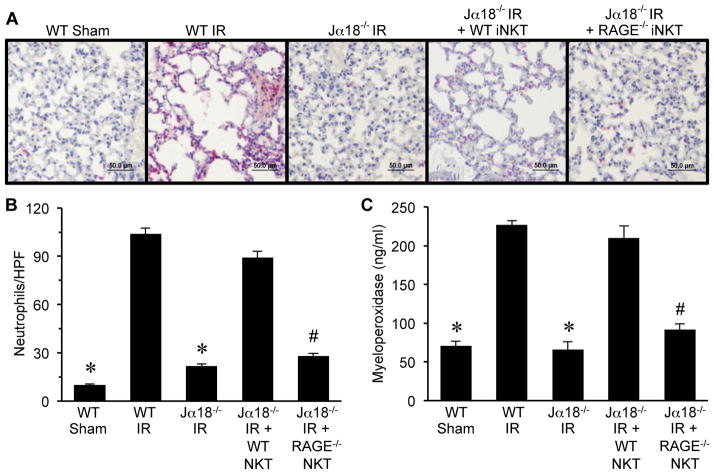
Figure 6. RAGE activation on iNKT cells mediates neutrophil infiltration and activation after IR.
Neutrophil infiltration and activation were assessed in lungs by immunohistochemistry and quantification of myeloperoxidase in BAL fluid. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry of lung sections. Neutrophils are stained red, sections are counterstained with hematoxylin, and images are at 40X magnification (bar=50 μm). (B) The number of neutrophils per high power field (neutrophils/HPF) was significantly increased after IR in WT mice (WT IR) versus sham (WT Sham) and was attenuated in Jα18−/− mice after IR (Jα18−/− IR). Neutrophil infiltration was restored after IR in Jα18−/− mice reconstituted with WT iNKT cells (Jα18−/− IR + WT NKT) but was significantly attenuated after IR in Jα18−/− mice reconstituted with RAGE−/− iNKT cells (Jα18−/− IR + RAGE−/− NKT). (C) Myeloperoxidase levels in BAL fluid were significantly increased in WT mice after IR and were attenuated in Jα18−/− mice after IR. Myeloperoxidase levels after IR were restored in Jα18−/− mice reconstituted with WT iNKT cells but were significantly attenuated after IR in Jα18−/− mice reconstituted with RAGE−/− iNKT cells. *P<0.05 versus WT IR, #P<0.05 versus Jα18−/− IR + WT NKT; n=5/group.